MIDI CC routing and radio
@Organism Here are the abstractions, it will ignore the first tick from the controller and just highlight the control to be edited and keep the CC value and the slider/numberbox2 up to date with each other so you can edit on the screen or with the controller and avoid all parameter jumps. The help file shows how to use the note data sent by the BeatSteps pads to switch what controls the encoder edits, but that can be switced to a radio or another CC like the tempo knob on the beatstep. As is this is setup to work with relative CCs centered on 64, but it would be simple to change it to work on other values,
@jameslo To my knowledge all of the Arturia controllers and sequencers can be set to send relative CC data, the one caveat is that if you do not have access to a Windows or Mac computer to run their software it can be difficult to change the controllers settings, Arturia has not been good about releasing the sysex for their gear and not all of their devices have had people figure out the sysex and post it on the web. Thankfully it is not hard to figure out the sysex, if you have access to a Windows or Mac machine at least. The regular BeatStep is the only device that I know of which has had someone do the work and publish the full sysex of on the web, I think one of the Keysteps has a good portion of its sysex posted, the rest just have bits and pieces scattered about.
PD's scheduler, timing, control-rate, audio-rate, block-size, (sub)sample accuracy,
@Nicolas-Danet said:
control messages and compute audio vectors of the DSP graph are interleaved operations. The internal audio vector size is 64.
[64][control][64][control][64][control][64][control]
Ok, i see.
But I read control messages are first, then audio. f.e. [loadbang] is proceeded before an upcoming audio-block.
And [vline~] is calculated and "drawn" before and "modulating" the *following * audio blocks.
[control][64][control][64][control][64][control][64]
What's happen in a 1 sample reblocked subpatch? In short, instead of compute 1 vector of 64 samples, it computes 64 times following a vector of 1 sample.
And there is no way to change this interval rate of 64?
Is upsampling in a subpatch increasing the computation time-interval of control-messages?
The tricky stuff with real time audio is not to do the things fast, but do things fast at the right time. Wait the sound in, deliver the sound out, compute the next sound and wait. When i benchmark my fork for instance, most of the time is spent in sleeping!
I see. In the analog world it is very different. This is why we have the buffer-latency in digital everywhere:
...incoming audio-samples in blocks, computation, audio out, and again...
And the control-domain every 64 samples.
For me as "user" of PD this is confusing.
So every object with a [v ...] will be sampleaccurate on point in upcoming audio-blocks, as long as it is not needed more often then 64 samples later!??? i.e. as long it is not starting several times in a smaller interval then 64 samples?
PD's scheduler, timing, control-rate, audio-rate, block-size, (sub)sample accuracy,
As already noticed, proceed the control messages and compute audio vectors of the DSP graph are interleaved operations. The internal audio vector size is 64.
[64][control][64][control][64][control][64][control]
What's happen in a 1 sample reblocked subpatch? In short, instead of compute 1 vector of 64 samples, it computes 64 times following a vector of 1 sample.
[1][1][1]...[1][1][1][control][1][1][1]...[1][1][1][control]
AFAIK, no messages is trigger faster than (very) roughly 1 ms (and that is true for the metro object also).
PD's scheduler, timing, control-rate, audio-rate, block-size, (sub)sample accuracy,
Hello, 
this is going to be a long one.
After years of using PD, I am still confused about its' timing and schedueling.
I have collected many snippets from here and there about this topic,
-wich all together are really confusing to me.
*I think it is very important to understand how timing works in detail for low-level programming … *
(For example the number of heavy jittering sequencers in hard and software make me wonder what sequencers are made actually for ? lol )
This is a collection of my findings regarding this topic, a bit messy and with confused questions.
I hope we can shed some light on this.


- a)
The first time, I had issues with the PD-scheduler vs. how I thought my patch should work is described here:
https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/11615/bang-bug-when-block-1-1-1-bang-on-every-sample
The answers where:
„
[...] it's just that messages actually only process every 64 samples at the least. You can get a bang every sample with [metro 1 1 samp] but it should be noted that most pd message objects only interact with each other at 64-sample boundaries, there are some that use the elapsed logical time to get times in between though (like vsnapshot~)
also this seems like a very inefficient way to do per-sample processing..
https://github.com/sebshader/shadylib http://www.openprocessing.org/user/29118
seb-harmonik.ar posted about a year ago , last edited by seb-harmonik.ar about a year ago
• 1
whale-av
@lacuna An excellent simple explanation from @seb-harmonik.ar.
Chapter 2.5 onwards for more info....... http://puredata.info/docs/manuals/pd/x2.htm
David.
“
There is written: http://puredata.info/docs/manuals/pd/x2.htm
„2.5. scheduling
Pd uses 64-bit floating point numbers to represent time, providing sample accuracy and essentially never overflowing. Time appears to the user in milliseconds.
2.5.1. audio and messages
Audio and message processing are interleaved in Pd. Audio processing is scheduled every 64 samples at Pd's sample rate; at 44100 Hz. this gives a period of 1.45 milliseconds. You may turn DSP computation on and off by sending the "pd" object the messages "dsp 1" and "dsp 0."
In the intervals between, delays might time out or external conditions might arise (incoming MIDI, mouse clicks, or whatnot). These may cause a cascade of depth-first message passing; each such message cascade is completely run out before the next message or DSP tick is computed. Messages are never passed to objects during a DSP tick; the ticks are atomic and parameter changes sent to different objects in any given message cascade take effect simultaneously.
In the middle of a message cascade you may schedule another one at a delay of zero. This delayed cascade happens after the present cascade has finished, but at the same logical time.
2.5.2. computation load
The Pd scheduler maintains a (user-specified) lead on its computations; that is, it tries to keep ahead of real time by a small amount in order to be able to absorb unpredictable, momentary increases in computation time. This is specified using the "audiobuffer" or "frags" command line flags (see getting Pd to run ).
If Pd gets late with respect to real time, gaps (either occasional or frequent) will appear in both the input and output audio streams. On the other hand, disk strewaming objects will work correctly, so that you may use Pd as a batch program with soundfile input and/or output. The "-nogui" and "-send" startup flags are provided to aid in doing this.
Pd's "realtime" computations compete for CPU time with its own GUI, which runs as a separate process. A flow control mechanism will be provided someday to prevent this from causing trouble, but it is in any case wise to avoid having too much drawing going on while Pd is trying to make sound. If a subwindow is closed, Pd suspends sending the GUI update messages for it; but not so for miniaturized windows as of version 0.32. You should really close them when you aren't using them.
2.5.3. determinism
All message cascades that are scheduled (via "delay" and its relatives) to happen before a given audio tick will happen as scheduled regardless of whether Pd as a whole is running on time; in other words, calculation is never reordered for any real-time considerations. This is done in order to make Pd's operation deterministic.
If a message cascade is started by an external event, a time tag is given it. These time tags are guaranteed to be consistent with the times at which timeouts are scheduled and DSP ticks are computed; i.e., time never decreases. (However, either Pd or a hardware driver may lie about the physical time an input arrives; this depends on the operating system.) "Timer" objects which meaure time intervals measure them in terms of the logical time stamps of the message cascades, so that timing a "delay" object always gives exactly the theoretical value. (There is, however, a "realtime" object that measures real time, with nondeterministic results.)
If two message cascades are scheduled for the same logical time, they are carried out in the order they were scheduled.
“
[block~ smaller then 64] doesn't change the interval of message-control-domain-calculation?,
Only the size of the audio-samples calculated at once is decreased?
Is this the reason [block~] should always be … 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1, nothing inbetween, because else it would mess with the calculation every 64 samples?
How do I know which messages are handeled inbetween smaller blocksizes the 64 and which are not?
How does [vline~] execute?
Does it calculate between sample 64 and 65 a ramp of samples with a delay beforehand, calculated in samples, too - running like a "stupid array" in audio-rate?
While sample 1-64 are running, PD does audio only?
[metro 1 1 samp]
How could I have known that? The helpfile doesn't mention this. EDIT: yes, it does.
(Offtopic: actually the whole forum is full of pd-vocabular-questions)
How is this calculation being done?
But you can „use“ the metro counts every 64 samples only, don't you?
Is the timing of [metro] exact? Will the milliseconds dialed in be on point or jittering with the 64 samples interval?
Even if it is exact the upcoming calculation will happen in that 64 sample frame!?
- b )


There are [phasor~], [vphasor~] and [vphasor2~] … and [vsamphold~]
https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/10192/vphasor-and-vphasor2-subsample-accurate-phasors
“Ive been getting back into Pd lately and have been messing around with some granular stuff. A few years ago I posted a [vphasor.mmb~] abstraction that made the phase reset of [phasor~] sample-accurate using vanilla objects. Unfortunately, I'm finding that with pitch-synchronous granular synthesis, sample accuracy isn't accurate enough. There's still a little jitter that causes a little bit of noise. So I went ahead and made an external to fix this issue, and I know a lot of people have wanted this so I thought I'd share.
[vphasor~] acts just like [phasor~], except the phase resets with subsample accuracy at the moment the message is sent. I think it's about as accurate as Pd will allow, though I don't pretend to be an expert C programmer or know Pd's api that well. But it seems to be about as accurate as [vline~]. (Actually, I've found that [vline~] starts its ramp a sample early, which is some unexpected behavior.)
[…]
“
- c)



Later I discovered that PD has jittery Midi because it doesn't handle Midi at a higher priority then everything else (GUI, OSC, message-domain ect.)
EDIT:
Tryed roundtrip-midi-messages with -nogui flag:
still some jitter.
Didn't try -nosleep flag yet (see below)
- d)

So I looked into the sources of PD:
scheduler with m_mainloop()
https://github.com/pure-data/pure-data/blob/master/src/m_sched.c
And found this paper
Scheduler explained (in German):
https://iaem.at/kurse/ss19/iaa/pdscheduler.pdf/view
wich explains the interleaving of control and audio domain as in the text of @seb-harmonik.ar with some drawings
plus the distinction between the two (control vs audio / realtime vs logical time / xruns vs burst batch processing).
And the "timestamping objects" listed below.
And the mainloop:
Loop
- messages (var.duration)
- dsp (rel.const.duration)
- sleep
With
[block~ 1 1 1]
calculations in the control-domain are done between every sample? But there is still a 64 sample interval somehow?
Why is [block~ 1 1 1] more expensive? The amount of data is the same!? Is this the overhead which makes the difference? Calling up operations ect.?
Timing-relevant objects
from iemlib:
[...]
iem_blocksize~ blocksize of a window in samples
iem_samplerate~ samplerate of a window in Hertz
------------------ t3~ - time-tagged-trigger --------------------
-- inputmessages allow a sample-accurate access to signalshape --
t3_sig~ time tagged trigger sig~
t3_line~ time tagged trigger line~
--------------- t3 - time-tagged-trigger ---------------------
----------- a time-tag is prepended to each message -----------
----- so these objects allow a sample-accurate access to ------
---------- the signal-objects t3_sig~ and t3_line~ ------------
t3_bpe time tagged trigger break point envelope
t3_delay time tagged trigger delay
t3_metro time tagged trigger metronom
t3_timer time tagged trigger timer
[...]
What are different use-cases of [line~] [vline~] and [t3_line~]?
And of [phasor~] [vphasor~] and [vphasor2~]?
When should I use [block~ 1 1 1] and when shouldn't I?
[line~] starts at block boundaries defined with [block~] and ends in exact timing?
[vline~] starts the line within the block?
and [t3_line~]???? Are they some kind of interrupt? Shortcutting within sheduling???
- c) again)

https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/1114/smooth-midi-clock-jitter/2
I read this in the html help for Pd:
„
MIDI and sleepgrain
In Linux, if you ask for "pd -midioutdev 1" for instance, you get /dev/midi0 or /dev/midi00 (or even /dev/midi). "-midioutdev 45" would be /dev/midi44. In NT, device number 0 is the "MIDI mapper", which is the default MIDI device you selected from the control panel; counting from one, the device numbers are card numbers as listed by "pd -listdev."
The "sleepgrain" controls how long (in milliseconds) Pd sleeps between periods of computation. This is normally the audio buffer divided by 4, but no less than 0.1 and no more than 5. On most OSes, ingoing and outgoing MIDI is quantized to this value, so if you care about MIDI timing, reduce this to 1 or less.
„
Why is there the „sleep-time“ of PD? For energy-saving??????
This seems to slow down the whole process-chain?
Can I control this with a startup flag or from withing PD? Or only in the sources?
There is a startup-flag for loading a different scheduler, wich is not documented how to use.
- e)

[pd~] helpfile says:
ATTENTION: DSP must be running in this process for the sub-process to run. This is because its clock is slaved to audio I/O it gets from us!
Doesn't [pd~] work within a Camomile plugin!?
How are things scheduled in Camomile? How is the communication with the DAW handled?
- f)

and slightly off-topic:
There is a batch mode:
https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/11776/sigmund-fiddle-or-helmholtz-faster-than-realtime/9
EDIT:
- g)
I didn't look into it, but there is:
https://grrrr.org/research/software/
clk – Syncable clocking objects for Pure Data and Max
This library implements a number of objects for highly precise and persistently stable timing, e.g. for the control of long-lasting sound installations or other complex time-related processes.
Sorry for the mess!
Could you please help me to sort things a bit? Mabye some real-world examples would help, too.

Midi controller not seen by Pd, but seen by system. Rpi3. Pd .49
@alexandros Thank you for your reply! Interesting. This worked. I had to launch Pd first then type in: aconnect 'Your Controller Name':0 'Pure Data':0
And that worked for Pd to receive midi data from my controller, but it didn't work for my controller to get messages from Pd (I have leds on my controller).
After some research I found aconnectgui, which is a gui to make midi connections.
After you install it you can launch it by typing aconnectgui in the terminal.
So I could connect everything that way, but that still won't work for me as I am going to use my Pi headless.
After more googling, I found I can just type the name of the midi client number in aconnect to make my connections. So for me that was:
aconnect 20:0 128:0
this connected my controller (20) to Pd (128)
To get Pd's midi out to my controller I had to do:
aconnect 128:1 20:0
Took a while but I figured it out.
Also, If my controller is plugged in when I turn on the Pi it is client number 20. If I plug it in later it's another number, so to keep it consistent I will always plug it in before i turn on the Pi.
It seems there is no way to save all these connections in Pd correct? My controller still is not showing up in the midi menu of Pd. So I guess I have to create a shell script or something to be fired up after Pd launches. If there is a way to save these setting in Pd please let me know.
Thank you for your help. If I can figure out this last bit I'll be set.
Final Solution: Anyone looking to control Ableton Live...easily
Hi All
A little bit of work to set up but forget midi mapping...google it if you dont believe me.
After a lot of time spent trying to get a simple but sophisticated way (using a minimal 8 button floorboard) to control Live on w10, I thought I would share this particular solution to possibly help others (especially after the help offered here on this forum). I tried a number of scenarios, even buying Max 4 Live, but it turns out a lot simpler than that. It needs 3 main areas set
FOOT CONTROLLER BEHAVIOURS/GESTURES
Create pd patch that gives you 'behaviours' per switch. Ill be happy to share mine but Im just cleaning them up atm.
eg I have 4 standard behaviours that dont take too much time to master
- Action A: A quick click (less than 500ms) Always the primary action
- Action B: Long click ie 1 click down and pedal up after 500ms. I use this eg always as a negative ramp down for things like lowering volume but if its just held down and released in a natural way, it is the secondary action of the switch
- Action C: 3 Click ie 1 quick down, up and then hold down. I use this for a positive ramp eg as volume up
4 Actiion D: Double click, Always a cancel
These are all mapped to note/ctrl outs that match the 'Selected Track Control' below
PLUGIN
Use PD VST to create a plugin version of your patch. This is loaded into Live as a control track. Live manages the connection of your floor board etc into the actual track so you dont wrestle with the io. I always use track 1 for click (forget Live metronome, this is much more flexible and can have feel/swing etc) so I dedicate track 2 to control.
Use LoopMIDI to create a virtual midi cable that will go from this track and be fed into the remote script.
REMOTE SCRIPT: 'Selected Track Control'
Download latest from http://stc.wiffbi.com/
Install to live and make sure your notes/control conform.
Enable this as a control surface in live and connect midi in from the plugin. Think about giving the guy a donation...massive amount of work and he deserves it!
I use it to control 8 tracks x 8 scenes and is controlled by 3 switches
- Scene control up and down (A = down, B = up)
- Track control same as scene
- Rec/Fire/Undo Volume up and down (A = fire/rec, B = Volume Down, C = Volume Up, D (Dbl Click) = Undo
The scenes and tracks wrap so there isnt too much foot tapping
There is quite a bit more to it of course...its and maybe no one else needs this but it would have saved me a couple of weeks of time so Im happy to help anyone wanting to achieve gigging without a massive floor rig and an easy way to map and remember.
HTH someone
Cheers
mark
Build a MIDI controller with the Arduino, Firmata and Pure Data
Time to start contributing some knowledge back to the wonderful world that is the internet; today, a step by step nice and easy tutorial on getting started to building your own MIDI controllers with the arduino.
When researching for my ableton controller project, I didn’t find much out there about using firmata on an arduino to send data to software. The standard approach just seemed to be create the code in the arduino language, upload it to your board and hack one of those MIDI to USB cables as a bodge job way of getting the MIDI out of the arduino.
So why firmata and pure data? Well the whole idea of firmata is that you flash it to your arduino, and it throws out serial about whats going on with the arduino inputs and outputs, then you decide how the software treats the readings coming in and going out.
Theory out the way, lets build some controllers. You’ll need a few things…
HARDWARE:
An arduino and something to wire into it (for this i’ll be using a pot)
A USB cable for your arduino
SOFTWARE:
Arduino – http://arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
Pure Data – http://puredata.info/downloads
Firmata – http://at.or.at/hans/pd/objects.html#pduino
Something to patch your new controller into; like Reason or Ableton Live
- SETTING UP FIRMATA AND PURE DATA
Install Pure Data and create a folder to store all your patches somewhere. Unzip Firmata and add the files ‘arduino.pd’, ‘arduino-test.pd’ and ‘arduino-help.pd’ to your new Pure Data folder. The ‘arduino.pd’ file is the object that we use in PD for opening up communication with your arduino and routing it to PD. Done? Awesome, your software is almost set up.
- FLASHING FIRMATA TO YOUR ARDUINO
Install the latest version of arduino and open it up. Connect your arduino with the USB cable to your laptop (i’m using a macbook for this by the way). In the example patches, open up “Standard Firmata”, select your board (im using an arduino mega), and your serial port (look for tty.usbserial for use with a USB cable). Then compile and hit the upload button and your arduino is now ready to use firmata and communicate with Pure Data!
- WIRING UP A POT
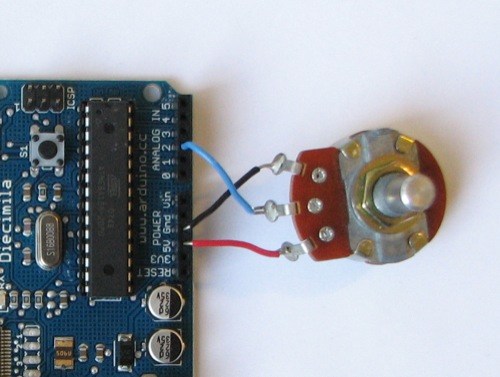
Potentiometers are cool, and theres a great arduino tutorial of how to wire one up here: http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Potentiometer
Basically, all you need to know is that there are three pins; your two outer pins govern voltage flow across the pot, meaning one has to be 5V and the other has to be ground. It doesn’t matter which, but your 5v pin is going to be where your pot reads maximum, so convention dictates this should be the right hand pin. The center pin needs to be connected to an analog in on the arduino and will read the value of the pot as it sweeps from ground (0v) to 5v.
All wired up? Plug it into your laptop and open Pure Data, we’re ready to get things talking.
- SETTING UP OUR PATCH
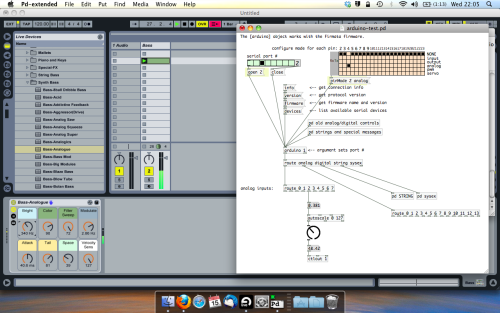
Open the example “arduino-test.pd” Pure Data patch you copied over earlier. It should look like this one…
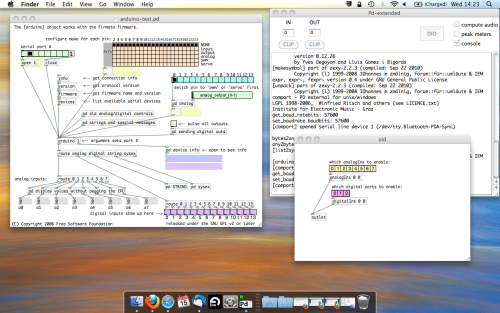
The test patch has everything we need to open a connection and enable pins. Firstly, lets delete a bunch of stuff and make our window a bit bigger. Hit Command + E to enter edit mode in Pure Data.
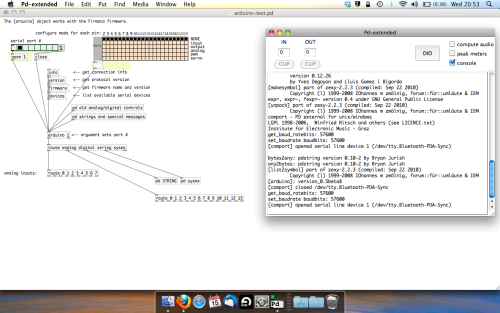
Ok a quick explaination; the key component here is the ‘arduino’ object. This is being drawn from the file you copied in earlier, and is what communicated with your arduino. Here we can do everything to control the arduino from opening a connection, to receiving data.
The large grid allows us to set the mode of each pin on the arduino. Remember pins 0 and 1 are reserved for Rx and Tx. I’m using analog pin 4 for this demo, so I’ve set my pin mode for pin 4 to ‘analog’.
Now we can plug our arduino in and get a reading from the potentiometer.
- ARDUINO INTO PURE DATA
With your arduino plugged in, hit command and E to bring us out of edit mode. In our patch, click on ‘Devices’ above the arduino object and open up the pure data terminal. (That other thing that loads with PD that has all the scary code in)
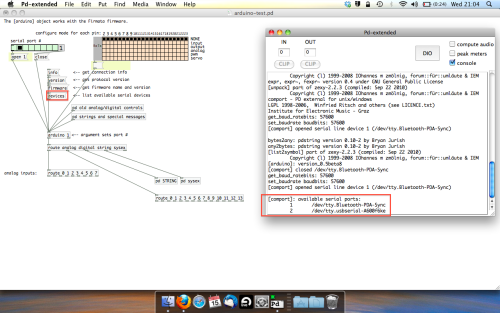
The “Devices” message connected to the arduino object pings your computer to find what devices are connected and on what serial ports. Since we’re using a USB cable to connect our arduino, we’re looking for something with ‘usbserial’ in it, in this case; port 2.
Select the relevent port in the green box at the top (remember the first box is ‘0’, second is ‘1’ and so forth) and hit ‘Open’ to establish a connection. Check the terminal to see if the connection was sucessful.
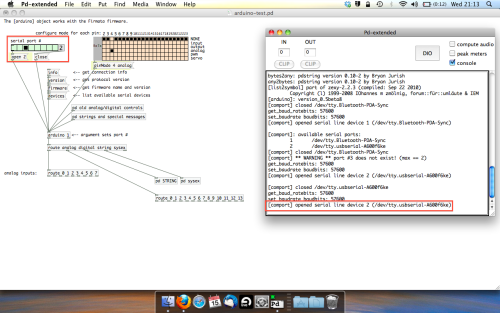
Now lets check we’re getting something in. Create a number box (Command + 3) and connect it to the relevent pin on the ‘Route analog’ box at the bottom. In this case, pin 4.
One more thing; if you’re not getting any readings in, you’ll need to click on ‘pd old analog/digital controls’ and enable your pins here too. What I tend to do in my patches is just not include the large grid but make my own ‘old pd’ controls custom to what i’m enabling/disabling to save space.
Here’s what the ‘old analog/digital controls’ subpatch looks like (pin 4 enabled)…
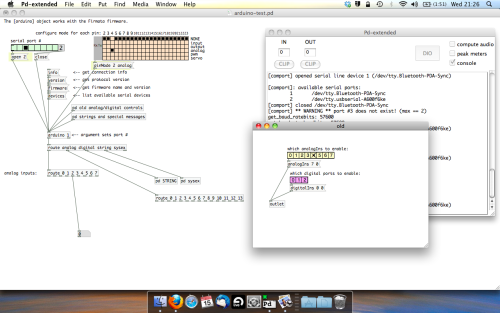
Come out of edit mode and check that you’ve got readings. If so congratulations! If not, troubleshoot, start with making sure your usb connection is opened, make sure all the correct pins are enabled (remember you’re counting from 0 not 1 on most of these buttons in PD, it’s just the way computers work).
- SCALING READINGS TO MIDI
So we’ve got a reading and chances are it’s to 3 decimal places between 0 to 1. No problem, create a new object (Command + 1) and type “autoscale 0 127”. This allows us to scale the input to a min and max value, in this case 0 to 127 of MIDI. Next, lets get things looking nice, create a new object and type “knob”. Connect this AFTER the autoscale object. (the knob is default set to read inputs from 0 to 127. Then create another number to display the scaled MIDI data coming out, and finally a new object and type “ctlout 1”.
It should look something like this…
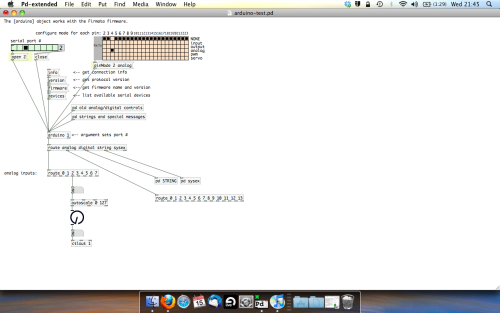
The second box should be outputing values from 0 – 127 now, and the knob giving a visual representation of your potentiometer.
Now lets patch it into ableton…
- PURE DATA TO ABLETON LIVE
Firstly, you’ll need to set up your macs IAC driver if you’ve not done this. Basically you’ll need to go into Audio/MIDI preferences and enable your IAC driver. Then create a new input and output. One for input to DAW and one for output from DAW. Google around for a tutorial on this, its really simple, a 30 second job.
After you’ve set up your IAC driver, go back to PD and go to preferences > MIDI Settings, and connect your IAC driver.
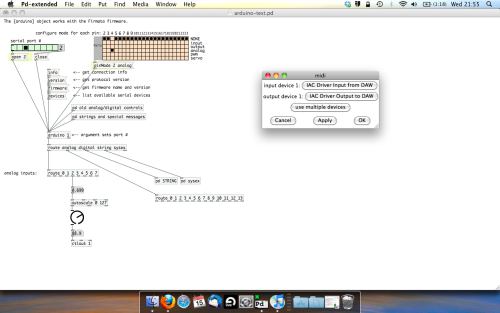
Open ableton and go to its MIDI preferences. Create a device listing for your IAC driver and enable its ins and outs into ableton like so…
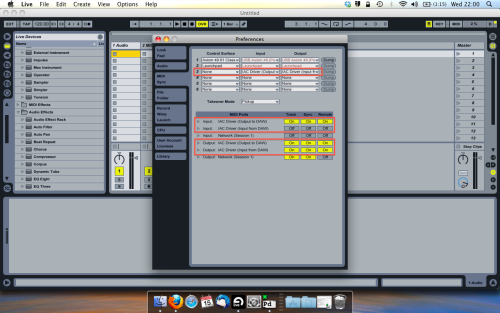
And thats it! Create an instrument and try to assign something! I’ve got it controlling the brightness of a bass sound here.
Shout out for Facu who requested this tutorial. Hopefully it’ll help some of you looking to get into this stuff and start building things but with no idea where to start.
Andúril (MobMuPlat app): fwd/bwd looper + 14 effects + elven cloak (control parameters via env~ and pitch as you play)
Andúril (MobMuPlat app): fwd/bwd looper + 14 effects + elven cloak (control parameters via env~ and pitch as you play)
UPDATED VERSION (corrected MobMuPlat system crash problem):
anduril.zip
This has been long in coming and I am very glad to finally release it (even tho my handheld hardware is not up to the job of running the elven cloak feature).
First a demo video and some screenshots, , and then the instructions.
DEMO VIDEO
SCREENSHOTS
Intention(s):
The app is designed to give (specifically a guitarist) tho really any input (even prerecorded as is the case in the demo (from: "Laura DeNardis Performing Pachabels Canon" from https://archive.org/details/LauraDenardisPerformingPachabelsCanon, specifically the wave file at: https://archive.org/download/LauraDenardisPerformingPachabelsCanon/PachabelsCanon.wav, Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0) FULL Control over the "voice" of their output-sound.
It includes:
a 5-band EQ (on page 2 of the app) (upfront that is applied to all incoming sounds);
a looper: with record, forward, backward, speed, and bypass controls (that runs via a throw along with the effects channel)
14 effects each with 3 controllable parameters (via the xy-slider+centered knob) including: chorus, distortion, delay, reverb, flanger, tremolo, vibrato, vcf, pitchshifter, pitchdelay, 12string, stepvibrato, pushdelay (delayfb driven by magnitude of the env~), and stagdelay (2 out-of-sync delay lines which can be driven in and out of phase by the sum of their delwrite+vd's so what goes in first may come out last)
elven_cloak: which drives the 3 parameter controls via the peak bands amplitude and proximity to a set pitch (midi note) and whose window can be broadened or shrunk and shifted within that window, i.e. the three effect parameters are changed automatically according to what and how you play
and
a tester synth: that randomly sends midi pitches between 20-108, velocities between 20-127, and durations between 250-500ms.
CONTROLS (from top-left to bottom-right):
PAGE 1:
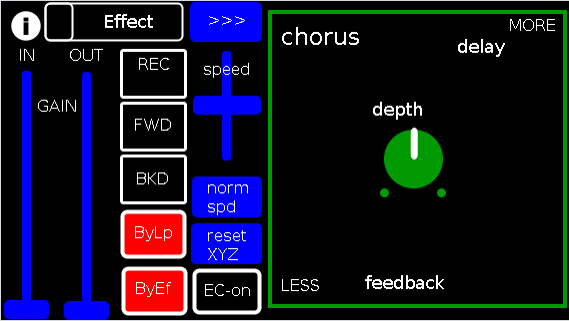
Effect: effects menu where the you choose an effect;
>>>,<<<: page navigation buttons;
IN,OUT: gains (IN is the preamp on the EQ5, and OUT is applied to total output);
REC,FWD,BWD,speed,normspd: the looper toggles and on speed, higher is faster and mid normal and normspd resets to mid;
xy-slider+centered knob: the 3 parameter controls + their labels (the bottom is x, top y and above the knob for the third one), the name of the selected effect and its parameters load each time you choose from the Effects menu, bottom left is lowest, top-right highest;
ByLp,ByEff: bypasses for the looper and effects "channel" (the outputs are summed);
EC-on: elven cloak toggle (default=off);
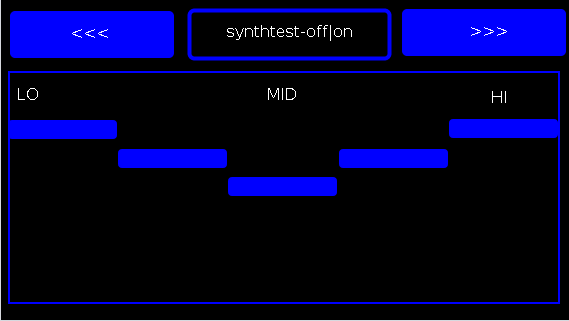
PAGE 2:
the EQ5 controls;
synthtest: off|on, default is off;
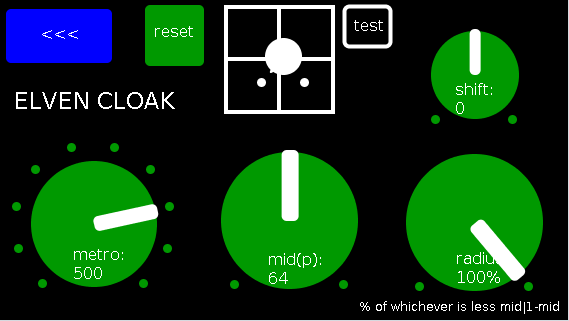
PAGE 3: elven cloak controls
reset: sets shift, metro, mid, and radius to 0, 500(ms),64,100% respectively (i.e. the entire midispectrum, 0-127) respectively;
mini-xyz, test: if test is on, you see a miniature representation of the xyz controls on the first page, so you can calibrate the cloak to your desired values;
shift: throws the center of the range to either the left or right(+/-1);
metro: how frequently in milliseconds to take env~ readings;
mid: the center in midipitch, i.e. 0-127, of the "watched" bands
radius(%): the width of the total bands to watch as a percentage of whichever is lower 1-mid or mid
END CONTROLS
Basic Logic:
There are 4 modes according to the bypass state of the looper and effects.
A throw catch and gain/sum/divide is applied accordingly.
End:
As I mentioned at the first, my handheld(s) are not good enough to let me use this but it runs great on my laptop.
So...
I would love to hear if this Does or Does Not work for others and even better any output others might make using it. I am enormously curious to hear what is "possible" with it.
Presets have not (yet  been included as I see it, esp. with the cloak as a tool to be used for improv and less set work. Tho I think it will work nicely for that too if you just turn the cloak off.
been included as I see it, esp. with the cloak as a tool to be used for improv and less set work. Tho I think it will work nicely for that too if you just turn the cloak off.
hmmm, hmmm,...
I think that's about it.
Let me know if you need any help, suggestions, ideas, explanations, etc. etc. etc. regarding the tool. I would be more than happy to share what I learned.
Peace, Love, and Ever-Lasting Music.
Sincerely,
Scott
p.s. please let me know if I did not handle the "attribution" part of "Laura DeNardis Performing Pachabels Canon" License correctly and I will correct it immediately.
Ciao, for now. Happy PD-ing!
The Harmonizer: Communal Synthesizer via Wifi-LAN and Mobmuplat
The Harmonizer: Communal Synthesizer via Wifi-LAN and Mobmuplat
The Harmonizer
The Harmonizer is a single or multi-player mini-moog synthesizer played over a shared LAN.
(credits: The original "minimoog" patch is used by permission from Jaime E. Oliver La Rosa at the the New York University, Music Department and NYU Waverly Labs (Spring 2014) and can be found at: http://nyu-waverlylabs.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/minimoog.zip)
One or more players can play the instrument with each player contributing to one or more copies of the synthesizer (via the app installed on each handheld) depending on whether they opt to play "player 1" or "player 2".
By default, all users are "player 1" so any changes to their app, ex. changing a parameter, playing a note, etc., goes to all other players playing "player 1".
If a user is "player 2", then their notes, controls, mod-wheel etc. are all still routed to the network, i.e. to all "player 1"'s, but they hear no sound on their own machine.
There are 2 pages in The Harmonizer. (See screenshots below.)
PAGE 1:
PAGE 2:
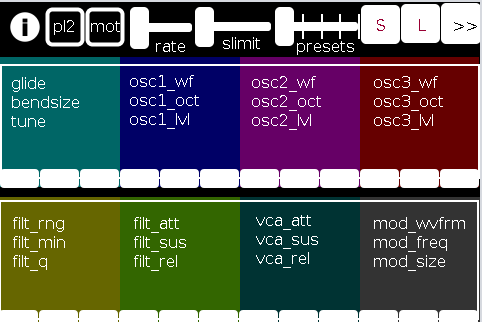
The first page of the app contains all controls operating on a (more or less) "meta"-level for the player: in the following order (reading top-left to bottom-right):
pl2: if selected (toggled) the user is choosing to play "player 2"
mot(ion): triggers system motion controls of the osc1,2&3 levels (volume) based on the accelerometer inside the smartphone (i.e as you twist and turn the handheld in your hand the 3 oscs' volumes change)
rate: how frequently should the handheld update its accelerometer data
slimit: by how much should the app slow down sending the (continuous) accelerometer data over the network
presets: from 1 to 5 preset "save-slots" to record and reload the Grid 1 and Grid 2 settings that are currently active
S: save the current Grid1 and Grid2 selections to the current "save slot"
L: load the currently selected preset into both Grids
">>": go the the next page (page 2 has the reverse, a "<<" button)
Grid 1: the settings, in 4 banks of 3 parameters per-, which are labeled top-down equating to left-right
Grid 2: the same as Grid 1, but with a different set of parameters
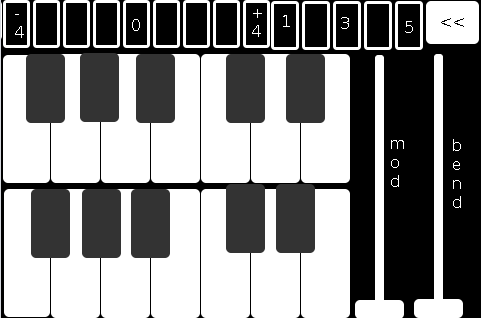
The second page comprises:
the 2-octave keyboard (lower notes on top),
a 9-button octave grid (which can go either up or down 4 octaves),
a quick-preset grid which loads one of the currently saved 5 presets
the "<<" button mentioned above, and
both a mod and pitch-bend wheel (as labeled).
SETUP:
All players install Mobmuplat;
Receive The Harmonizer (in the form of a .zip file either via download or thru email, etc.)
When on your smartphone, click on the zip file, for example, as an attachment in an email.
Both android and iphone will recognize (unless you have previously set a default behavior for .zip files) the zip file and ask if you would like to open it in Mobmuplat. Do so.
When you open Mobmuplat, you will be presented with a list of names, if in android click the 3 dots in the top right of the window and on the settings window , click "Network" Or on an iphone click "Network" just below the name list;
On the Network tab, click "LANDINI".
Switch "LANDINI" from "off" to "on".
(this will allow you to send your control data over your local area network with anyone else who is on that same LAN).
From that window, click "Documents".
You will be presented again, with the previous list of names.
Scroll down to "TheHarmonizer" and click on it.
The app will open to Page 1 as described and shown in the image above.
Enjoy with Or without Friends, Loved, Ones, or just folks who want to know what you mean "is possible" with Pure Data  )!
)!
Theories of Thought on the Matter
My opinion is:
While competition could begin over "who controls" the song, in not too great a deal of time, players will see first hand, that it is better (at least in this case) to work together than against one another.
If any form of competition emerges in the game, for instance loading a preset when a another player was working on a tune or musical idea, the Overall playablilty and gratitude-level will wain.
However, on the other hand, if players see the many, many ways one can constructively collaborate I think the rewards will be far more measurable than the costs, for instance, one player plays notes while the other player plays the controls.
p.s. my thinking is:
since you can play solo: it will be fun to create cool presets when alone then throw them into the mix once you start to play together. (Has sort of a card collecting fee  ).
).
Afterward:
This was just too easy Not to do.
It conjoins many aspects of pure data together (I have been working on lately (afterward: i did this app a long time ago but for some reason and am only now thinking to share it) both logistical and procedural into a single whole.
I think it does both quite well, as well as, offer the user an opportunity to consider or perhaps even wonder: What is 'possible'?"
Always share. Life is just too damn short not to.
Love only.
-svanya
Audio Ideas (AI) Collection (placeholder, currently only links)-effects, controllers, mmp, etc.
Audio Ideas (AI) Collection (placeholder) currently only links
per @LiamG 's kind suggestion I have begun the process of consolidating my abs and patches, etc. into a single location/zip file or for possible upload to github.
Just to get the ball/me rolling and scope the work I got the links for my shares into a single location to later be consolidated into the single AI Collection.
For now at least, please, bare with me (and the links below) as ideas I am more passionate about currently are demanding my attention. (Which  funnily enough will probably also be included in the set, where ever they are shared.)
funnily enough will probably also be included in the set, where ever they are shared.)
Thanks, for your patience and all you do for the Pure Data Family.
Sincerely,
Scott
abstract~
pushdelay-envelope-env-driven-delay-line-with-both-delay-time-and-feedback-dependent
numpad-abstraction-for-entry-of-large-numbers-via-click-instead-of-sliders-includes-basic-calculator
abs_delay_fbw-feedbackwards-lifo-last-in-first-out-delay
abs_sequences_by_formula-sequences-by-formula-abstraction-ex-collatz
abs_effects_router-60-effects-in-one-abstraction-router-from-diy2-stamp-album-my-abs
visualcontrolsurface-vsl-values-set-by-their-location-on-the-screen-req-ggee-shell
abs_4-8-14_way_toggle-pair-2-toggles-resulting-in-4-8-or-14-states
audioflow-delay-to-forward-backward-looper-using-speed-control
5-band-equalizer-with-bezier-controller-eq5_mey_w_bezier_sv-pd-updated-to-8-band-below
forward-backward-looper-orig-abs-from-residuum-whale-av
abs_rgb2hex-rgb-0-255-colors-to-hexadecimal-values
pseudo-12-string-effect-6-string-guitar-to-sound-like-a-12-string
jack_midi2pd_2sys_connector_sv-jack-midi_out-to-pd-sys_playback-switcher
abs_4to16pads_bin_conv_sv-convert-4-midi-pads-from-a-binary-value-to-a-decimal-for-rerouting
abs_automatedslider_sv-automated-control-changer-pd-and-mobmuplat-editor-versions
idea-for-effects-stack-ing-technique-control-mother
micin-_abs-abstraction-convert-signal-to-notein-ex-using-a-midi-synth-as-a-guitar-pedal
curve_abs-tri-way-curve-switch-to-change-control-values-in-either-linearly-convex-or-concave-manner
a-preset-control-abstraction-for-saving-parameters-presets-to-text-files
4-tap-delay-with-pitch-shifter-per-delay-line-adaptation-of-diy2-patches
patch~
extra
the-15-owl-faust-patches-compiled-as-32bit-linux-externals-attached
libpd
mmponboardeditortemplate-mmp-for-creation-of-mobmuplat-files-directly-on-the-handheld-android-only
3d-synth-webpd-tree-js-webgl_camera_cinematic-html-example
Off topic