PD's scheduler, timing, control-rate, audio-rate, block-size, (sub)sample accuracy,
@EEight said:
@lacuna said:
I just see this flag on linux:
-nosleep -- spin, don't sleep (may lower latency on multi-CPUs)
Oh yes and there are startup flags for loading a different scheduler (I corrected this in my first post now)
https://puredata.info/docs/faq/commandline
-rt or -realtime -- use real-time priority
-nrt -- don't use real-time priority
-sleep -- sleep when idle, don't spin (true by default)
-nosleep -- spin, don't sleep (may lower latency on multi-CPUs)
-schedlib <file> -- plug in external scheduler
-extraflags <s> -- string argument to send schedlib
-batch -- run off-line as a batch process
-nobatch -- run interactively (true by default)
Not sure, would be interested to know too.
@EEight output of full text search of sleep with grep in pd's source folder -nri flags set:
https://pastebin.com/3mBw6Mnj
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/u_pdsend.c:86: sleep (nretry < 5 ? 1 : 5);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_stuff.h:65:extern int sys_sleepgrain;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_stuff.h:163:EXTERN void sys_microsleep(int microsec);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_stuff.h:369:EXTERN int* get_sys_sleepgrain(void);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:58:int sys_nosleep = 0; /* skip all "sleep" calls and spin instead */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:115:int* get_sys_sleepgrain() { return &sys_sleepgrain; }
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:424:"-sleepgrain <n> -- specify number of milliseconds to sleep when idle\n",
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:520:"-sleep -- sleep when idle, don't spin (true by default)\n",
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:521:"-nosleep -- spin, don't sleep (may lower latency on multi-CPUs)\n",
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:732: else if (!strcmp(*argv, "-sleepgrain"))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:737: sys_sleepgrain = 1000 * atof(argv[1]);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1242: else if (!strcmp(*argv, "-sleep"))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1244: sys_nosleep = 0;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1247: else if (!strcmp(*argv, "-nosleep"))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1249: sys_nosleep = 1;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:202:extern int sys_nosleep;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:204:/* sleep (but cancel the sleeping if pollem is set and any file descriptors are
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:207:sleep. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:208:static int sys_domicrosleep(int microsec, int pollem)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:226: perror("microsleep select");
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:242: Sleep(microsec/1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:244: usleep(microsec);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:251: /* sleep (but if any incoming or to-gui sending to do, do that instead.)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:253:void sys_microsleep(int microsec)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:256: sys_domicrosleep(microsec, 1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:909: int didsomething = sys_domicrosleep(0, 1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:16: correct thread synchronization (by defining THREADSIGNAL) or just sleeping
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:21: switch to usleep in s_inter.c
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:91:#include <windows.h> /* for Sleep() */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:549: sys_microsleep(sys_sleepgrain);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:550: if (!pa_stream) /* sys_microsleep() may have closed device */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:591: sys_microsleep(sys_sleepgrain);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:592: if (!pa_stream) /* sys_microsleep() may have closed device */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_oss.c:672: sys_microsleep(2000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:105:/* if more than this sleep detected, should be more than periodsize/samplerate ??? */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:106:static double sleep_time;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:340: sleep_time = (float) alsamm_period_size/ (float) alsamm_sr;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:798: sleep(1); /* wait until the suspend flag is released */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:1336: if ((timenow = sys_getrealtime()) > (timelast + sleep_time))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:1342: timenow,timelast,sleep_time,(timelast + sleep_time));
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsa.c:691: sys_microsleep(5000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:23:int sys_usecsincelastsleep(void);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:24:int sys_sleepgrain;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:442:will now sleep. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:454: if (sys_sleepgrain < 100)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:455: sys_sleepgrain = sys_schedadvance/4;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:456: if (sys_sleepgrain < 100)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:457: sys_sleepgrain = 100;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:458: else if (sys_sleepgrain > 5000)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:459: sys_sleepgrain = 5000;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:477: the machine sleeps. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:539: /* if even that had nothing to do, sleep. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:541: sys_microsleep(sys_sleepgrain);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:574: Sleep(1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:576: sleep(1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptwinmm.c:67:PMEXPORT void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptwinmm.c:69: Sleep(duration);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_mach.c:128:void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_mach.c:130: usleep(duration * 1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_cf.c:137:void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_cf.c:139: usleep(duration * 1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptlinux.c:14:of sleeping when realtime threads request a sleep of <=2ms (as a way
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptlinux.c:132:void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptlinux.c:134: usleep(duration * 1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/porttime.h:82: Pt_Sleep() pauses, allowing other threads to run.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/porttime.h:88:PMEXPORT void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/pm_mac/pmmacosxcm.c:492: usleep((useconds_t)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/patches/mac_limit_rate_override.patch:52: usleep((useconds_t)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/win/pa_win_util.c:102:void Pa_Sleep( long msec )
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/win/pa_win_util.c:104: Sleep( msec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:108:void Pa_Sleep( long msec )
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:110:#ifdef HAVE_NANOSLEEP
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:116: nanosleep(&req, &rem);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:117: /* XXX: Try sleeping the remaining time (contained in rem) if interrupted by a signal? */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:120: { /* to usleep must be < 1000000. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:121: usleep( 999000 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:124: usleep( msec * 1000 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:599: /* Test before and after in case whatever underlying sleep call isn't interrupted by pthread_cancel */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:601: Pa_Sleep( intervalMsec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:644: PA_DEBUG(( "%s: Watchdog sleeping for %lu msecs before unthrottling\n", __FUNCTION__, th->throttledSleepTime ));
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:645: Pa_Sleep( th->throttledSleepTime );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:704: Pa_Sleep( intervalMsec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:2185: unsigned long throttledSleepMsecs;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:2565: /* time to sleep when throttling due to >100% cpu usage.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:2567: stream->throttledSleepMsecs =
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:3194: /* sleep to give other processes a go */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:3195: Sleep( stream->throttledSleepMsecs );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_utilities.c:395: /* No match yet, so let's sleep and try again. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_utilities.c:396: Pa_Sleep( 100 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.h:69:#define PA_MAC_BLIO_BUSY_WAIT_SLEEP_INTERVAL (5)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.c:454: Pa_Sleep( PA_MAC_BLIO_BUSY_WAIT_SLEEP_INTERVAL );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.c:535: Pa_Sleep( PA_MAC_BLIO_BUSY_WAIT_SLEEP_INTERVAL );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.c:607: Pa_Sleep( msecPerBuffer );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core.c:2722: Pa_Sleep( 100 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/asio/pa_asio.cpp:3401: Sleep(1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:1129: Pa_Sleep( 10 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:2759: /* self->threading.throttledSleepTime = (unsigned long) (minFramesPerHostBuffer / sampleRate / 4 * 1000); */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:3831: Pa_Sleep( 1 ); /* avoid hot loop */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:3849: if( timeouts > 1 ) /* sometimes device times out, but normally once, so we do not sleep any time */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:3851: Pa_Sleep( 1 ); /* avoid hot loop */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/common/pa_util.h:152:/* void Pa_Sleep( long msec ); must also be implemented in per-platform .c file */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/portaudio.h:1211:/** Put the caller to sleep for at least 'msec' milliseconds. This function is
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/portaudio.h:1215: The function may sleep longer than requested so don't rely on this for accurate
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/portaudio.h:1218:void Pa_Sleep( long msec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/pa_win_wmme.h:64: to THREAD_PRIORITY_NORMAL and sleeps the thread if the CPU load exceeds 100%
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/pa_linux_alsa.h:91:/** Set the maximum number of times to retry opening busy device (sleeping for a
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:599:<P> In linux, a "-nosleep" flag causes Pd to poll instead of sleeping as it
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:798:<P> Fixed a thread-safety problem in sys_microsleep().
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:1224:the controlling parameter for MIDI jitter is "-sleepgrain", which specifies
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:1225:the interval of time Pd sleeps when it believes it's idle.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:1373:<P> -sleepgrain: if you aren't using audio I/O, this can reduce time jitter in
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:488:scheduling; "-sleepgrain 1" sets the sleep grain to 1 (see under MIDI below),
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:489:and typing "-rt -sleepgrain 1" does both.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:527:-sleepgrain <n> -- specify number of milliseconds to sleep when idle
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:573:-nosleep -- never relinquish CPU (only for multiprocessors!)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:610:<H4> MIDI and sleepgrain</H4>
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:619:<P> The "sleepgrain" controls how long (in milliseconds) Pd sleeps between
good night sweet dreams
abl_link~ midi and audio sync setup
Hi Folks,
I thought I’d share this patch in the hopes that someone might be able to help improve upon it. I am by no means even semi competent with PD and jumped into this task without actually bothering to learn the basics of PD or RPi, but nevertheless here we are: maybe you can share a better implementation.
Mods/experienced folks, if I am sharing irrelevant/wrong/confusing info, mea culpa and please correct me.
I wanted to make a patch for PD in Raspberry Pi that would do 3 things:
- Get the abl_link~ temp data over wifi
- Create a midi clock output using a 5-pin midi adapter (I have one of the cheapo usb-to-midi cable things here)
-simultaneously create an audio pulse ‘clock’ output such as those used by volcas, Teenage Engineering Pocket operators, and the like (I am not sure if such an audio signal over a 3.5mm jack would be hot enough to be considered a CV pulse too, maybe you can help clear that up?)
As I say, after much struggles I have globbed something together that sort of does this.
A couple of things for newcomers like myself:
The abl_link~ object in the patch isn’t initially part of the standard pure data install as I write. I was able to use deken (ie the code that powers the ‘help/find externals’ bit of PD) to look for abl_link~. Search for it. At the time of writing there is a version for Arm7 devices like the Raspberry Pi 3 which was put together by the illustrious mzero with code from antlr. Go ahead and install the abl_link~ object. (Possibly you may have to uncheck the ‘hide foreign architectures’ box to get the arm7 version to show up. This is usually a safeguard to stop users from trying to install versions of externals that won’t work on their systems. So long as you see ‘arm7’ in the description it should hopefully be the one you want) PD will ask where you want to store the external, and I would just leave it at the default unless you have a special reason to do otherwise.
To get the patch to hook up to your preferred audio and midi outputs by default you may have to take certain steps. In my version of it I have deemed the built in audio and my cheapo USB midi output to be good enough for this task.
[As part of my troubleshooting process I ended up installing amidiauto which is linked to here: https://community.blokas.io/t/script-for-launching-pd-patch-with-midi-without-aconnect/1010/2
I undertook several installations in support of amidiauto which may be helping my system to see and link up my USB midi and PD, but nothing worked until I took the step in the following paragraph about startup flags in PD. (It may also be that I did not need to put in amidiauto at all. Maybe I’ll try that on another card to see if it simplifies the process. I’m saying you might want to try it without amidiauto first to see).]
Midi: - (ALSA is the onboard audio and midi solution that is part of Raspbian). To have PD use ALSA midi at the start I made the following setting in the preferences/startup dialog - within that window there is a section (initially blank) for startup flags. Here you can set instructions for PD to take note of when it starts up. I put in -alsamidi to tell it that alsamidi will be my preferred midi output. (I also took the step of going to file/preferences/midi settings, then ‘apply’ and ‘ok’ to confirm the Alsa midi ports that showed up. Then I went back to file/preferences/save all preferences. This seems to have (fingers crossed) saved the connection to my USB midi output.
Audio: I used the terminal and sudo raspi-config to set my audio out to the internal sound card (advanced options/audio/3.5mm jack). Since I had a fairly unused installation of PD I’d never asked it to do anything but work with the system defaults so getting audio out was fairly simple.
[nb I initially stuck this patch together on my Mac where everything worked pretty trouble free in terms of audio and midi selection]
About the patch. Obviously it is sort of horrible but there it is. It is a combination of stuff I cribbed from the demo example of abl_link~ in the example, and two example patches created by users NoDSP and jpg in this forum post https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/9545/generate-midi-clock-messages-from-pd/2
As well as some basic synthesis to make the bip bip noises I learned from LWMs youtube channel
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCw5MbnaoDDuRPFsqaQpU9ig
Any and all errors and bad practice are mine alone.
The patch has some comments in it that doubtless expose my own lack of understanding more than anything. Undoubtedly many users can do a better job than I can.
Some observations on limitations/screwups of the patch:
-
If you disconnect from the stream for a bit, it will attempt to catch up. There will be a massive flurry of notes and/or audio bips as it plays all the intervening notes.
-
It doesn’t seem to be too fussy about where in the bar it is getting started (It will be "on" the beat but sometimes the ‘1’will be the ‘2’ etc. This is okay if I’m using internal sequencers from scratch (in the volca, say) but not if there is an existing pattern that I am trying to have come in 'on the 1'.
-
My solution to more detailed subdivision of bars was to make a big old list of numbers up to 32 so that abl_link~ can count up to more than 4. There’s probably a better solution for this. If you find that you need even more subdivisions because you are making some sort of inhumanly manic speed gabba, add even yet more numbers and connections.
I haven’t tested this much. And since it’s taken me the better part of 18 months to do this at all, I’m really not your guy to make it work any better. I’m posting here so that wiser souls can do a better job and maybe share what I think has the potential to be a useful midi sync tool.
I plan to revisit https://community.blokas.io/t/script-for-launching-pd-patch-with-midi-without-aconnect/1010/3
for some pointers on setting this up to launch the patch at startup to give me a small, portable midi Link sync device for 5-pin and audio-pulse clocked devices.
This is my first ever bit of quasi productive input to any technical community (mostly I just hang around asking dumb questions… So be kind and please use your giant brains to make it better) I look forward to spending some time learning the basics now.  link-sync.pd
link-sync.pd
gem pix_film playback inconsistency issues
hellooooo
I am programming a simple patch (on mac osx) to link a temperature sensor data trigger via arduino to video playback with gem and having various issues getting the video to open and playback consistently. I've gotten the patch to work successfully occasionally by reseting the video file (through changing it to an .aiv file, running the patch without success, then changing the file back to .mov and running the patch with success) however this manual reset only works once and then i encounter the below issues when trying to run the patch again.
my first issue is that often the video file will open with (auto 1)--[pix_film] and only show a still frame image from the file without playing through, so i have to manually close [gemwin] instead of the third outlet bang from [pix_film] routing to [destroy], resetting [oneshot] to allow the bang to be triggered again, and resetting the toggle-- (auto 1)
my second issue is the most often the initial [trigger bang bang] that I've routed to simultaneously (create)--[gemwin], and toggle the (auto 1)--[pix_film file.mov] will instantly route to the finished [bang] on the third outlet of [pix_film] without opening [gemwin] or playing back the video at all, though the toggle will be activated until I manually turn it off.
since the patch works successfully sometimes for one round of -- opening window turning on the toggle-running playback-closing window and turning off the toggle-- i am wondering if there is a necessary message to reset [pix_film file.mov] in order to get the patch to work cyclically
any help would be greatly appreciated asap as im planning to utilize the patch live tonight
[small job offer] porting max external to pd
Edit 1: Took a shot porting it in this little textarea. Probably doesn't compile yet...
Edit 2: Ok, this should compile now. I haven't actually tried to instantiate it yet, though. It's possible I set it up with the wrong number of xlets.
Edit 3: Seems to instantiate ok. It appears it doesn't take signal input so the CLASS_MAINSIGNALIN macro is neccessary. Just comment that part out to make it a control signal.
Note-- in my port it's called [vb_fourses~] for the reason noted below.
I have no idea if the algorithm behaves correctly, but it does output sound.
Btw-- AFAICT you should be able to compile this external for the 64-bit version of Purr Data and it should work properly. It doesn't require a special 64-bit codepath in Pd so I commented that part out.
Btw 2-- there should probably be a "best practices" rule that states you can only name your class something that is a legal C function name. Because this class doesn't follow that practice I made a mistake in the port. Further, the user will make a mistake because I had to change the class name. If I had instead made the setup function a different name than the creator I would create an additional problem that would force users to declare the lib before using it. Bad all around, and not worth whatever benefit there is to naming a class "foo.bar" instead of "foo_bar"
/*
#include "ext.h"
#include "ext_obex.h"
#include "z_dsp.h"
#include "ext_common.h"
*/
#include "m_pd.h"
#include "math.h"
/*
a chaotic oscillator network
based on descriptions of the 'fourses system' by ciat-lonbarde
www.ciat-lonbarde.net
07.april 2013, volker b?hm
*/
#define NUMFOURSES 4
static void *myObj_class;
typedef struct {
// this is a horse... basically a ramp generator
double val;
double inc;
double dec;
double adder;
double incy, incym1; // used for smoothing
double decy, decym1; // used for smoothing
} t_horse;
typedef struct {
t_object x_obj;
double r_sr;
t_horse fourses[NUMFOURSES+2]; // four horses make a fourse...
double smoother;
t_sample x_f;
} t_myObj;
// absolute limits
static void myObj_hilim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input);
static void myObj_lolim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input);
// up and down freqs for all oscillators
static void myObj_upfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4);
static void myObj_downfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4);
static void myObj_smooth(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input);
static void myObj_info(t_myObj *x);
// DSP methods
static void myObj_dsp(t_myObj *x, t_signal **sp);
static t_int *myObj_perform(t_int *w);
//void myObj_dsp64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, short *count, double samplerate,
// long maxvectorsize, long flags);
//void myObj_perform64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, double **ins, long numins,
// double **outs, long numouts, long sampleframes, long flags, void *userparam);
//
static void *myObj_new( t_symbol *s, int argc, t_atom *argv);
//void myObj_assist(t_myObj *x, void *b, long m, long a, char *s);
void vb_fourses_tilde_setup(void) {
t_class *c;
myObj_class = class_new(gensym("vb_fourses~"), (t_newmethod)myObj_new, 0, sizeof(t_myObj),
0, A_GIMME, NULL);
c = myObj_class;
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_dsp, gensym("dsp"), A_CANT, 0);
// class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_dsp64, gensym("dsp64"), A_CANT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_smooth, gensym("smooth"), A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_hilim, gensym("hilim"), A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_lolim, gensym("lolim"), A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_upfreq, gensym("upfreq"), A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_downfreq, gensym("downfreq"), A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_info, gensym("info"), 0);
//class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_assist, "assist", A_CANT,0);
CLASS_MAINSIGNALIN(myObj_class, t_myObj, x_f);
// class_dspinit(c);
// class_register(CLASS_BOX, c);
post("vb_fourses~ by volker b?hm\n");
// return 0;
}
static void myObj_smooth(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input) {
// input = CLAMP(input, 0., 1.);
if (input < 0.) input = 0;
if (input > 1.) input = 1;
x->smoother = 0.01 - pow(input,0.2)*0.01;
}
static void myObj_hilim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input) {
x->fourses[0].val = input; // store global high limit in fourses[0]
}
static void myObj_lolim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input) {
x->fourses[5].val = input; // store global low limit in fourses[5]
}
static void myObj_upfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4) {
x->fourses[1].inc = fabs(freq1)*4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[2].inc = fabs(freq2)*4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[3].inc = fabs(freq3)*4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[4].inc = fabs(freq4)*4*x->r_sr;
}
static void myObj_downfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4) {
x->fourses[1].dec = fabs(freq1)*-4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[2].dec = fabs(freq2)*-4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[3].dec = fabs(freq3)*-4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[4].dec = fabs(freq4)*-4*x->r_sr;
}
//#pragma mark 64bit dsp-loop ------------------
//void myObj_dsp64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, short *count, double samplerate,
// long maxvectorsize, long flags) {
// object_method(dsp64, gensym("dsp_add64"), x, myObj_perform64, 0, NULL);
//
// if(samplerate<=0) x->r_sr = 1.0/44100.0;
// else x->r_sr = 1.0/samplerate;
//
//
//}
//static void myObj_perform64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, double **ins, long numins,
// double **outs, long numouts, long sampleframes, long flags, void *userparam){
//
// t_double **output = outs;
// int vs = sampleframes;
// t_horse *fourses = x->fourses;
// double val, c, hilim, lolim;
// int i, n;
//
// if (x->x_obj.z_disabled)
// return;
//
// c = x->smoother;
// hilim = fourses[0].val;
// lolim = fourses[5].val;
//
// for(i=0; i<vs; i++)
// {
// for(n=1; n<=NUMFOURSES; n++) {
// // smoother
// fourses[n].incy = fourses[n].inc*c + fourses[n].incym1*(1-c);
// fourses[n].incym1 = fourses[n].incy;
//
// fourses[n].decy = fourses[n].dec*c + fourses[n].decym1*(1-c);
// fourses[n].decym1 = fourses[n].decy;
//
// val = fourses[n].val;
// val += fourses[n].adder;
//
// if(val <= fourses[n+1].val || val <= lolim ) {
// fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].incy;
// }
// else if( val >= fourses[n-1].val || val >= hilim ) {
// fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].decy;
// }
//
// output[n-1][i] = val;
//
// fourses[n].val = val;
// }
// }
//
// return;
//
//}
//#pragma mark 32bit dsp-loop ------------------
static void myObj_dsp(t_myObj *x, t_signal **sp)
{
dsp_add(myObj_perform, 6, x, sp[0]->s_vec, sp[1]->s_vec, sp[2]->s_vec, sp[3]->s_vec, sp[0]->s_n);
if(sp[0]->s_sr<=0)
x->r_sr = 1.0/44100.0;
else x->r_sr = 1.0/sp[0]->s_sr;
}
static t_int *myObj_perform(t_int *w)
{
t_myObj *x = (t_myObj*)(w[1]);
t_float *out1 = (float *)(w[2]);
t_float *out2 = (float *)(w[3]);
t_float *out3 = (float *)(w[4]);
t_float *out4 = (float *)(w[5]);
int vs = (int)(w[6]);
// Hm... not sure about this member. I don't think we can disable individual
// objects in Pd...
// if (x->x_obj.z_disabled)
// goto out;
t_horse *fourses = x->fourses;
double val, c, hilim, lolim;
int i, n;
c = x->smoother;
hilim = fourses[0].val;
lolim = fourses[5].val;
for(i=0; i<vs; i++)
{
for(n=1; n<=NUMFOURSES; n++) {
// smoother
fourses[n].incy = fourses[n].inc*c + fourses[n].incym1*(1-c);
fourses[n].incym1 = fourses[n].incy;
fourses[n].decy = fourses[n].dec*c + fourses[n].decym1*(1-c);
fourses[n].decym1 = fourses[n].decy;
val = fourses[n].val;
val += fourses[n].adder;
if(val <= fourses[n+1].val || val <= lolim ) {
fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].incy;
}
else if( val >= fourses[n-1].val || val >= hilim ) {
fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].decy;
}
fourses[n].val = val;
}
out1[i] = fourses[1].val;
out2[i] = fourses[2].val;
out3[i] = fourses[3].val;
out4[i] = fourses[4].val;
}
//out:
return w+7;
}
static void myObj_info(t_myObj *x) {
int i;
// only fourses 1 to 4 are used
post("----- fourses.info -------");
for(i=1; i<=NUMFOURSES; i++) {
post("fourses[%ld].val = %f", i, x->fourses[i].val);
post("fourses[%ld].inc = %f", i, x->fourses[i].inc);
post("fourses[%ld].dec = %f", i, x->fourses[i].dec);
post("fourses[%ld].adder = %f", i, x->fourses[i].adder);
}
post("------ end -------");
}
void *myObj_new(t_symbol *s, int argc, t_atom *argv)
{
t_myObj *x = (t_myObj *)pd_new(myObj_class);
// dsp_setup((t_pxobject*)x, 0);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
x->r_sr = 1.0/sys_getsr();
if(sys_getsr() <= 0)
x->r_sr = 1.0/44100.f;
int i;
for(i=1; i<=NUMFOURSES; i++) {
x->fourses[i].val = 0.;
x->fourses[i].inc = 0.01;
x->fourses[i].dec = -0.01;
x->fourses[i].adder = x->fourses[i].inc;
}
x->fourses[0].val = 1.; // dummy 'horse' only used as high limit for fourses[1]
x->fourses[5].val = -1.; // dummy 'horse' only used as low limit for fourses[4]
x->smoother = 0.01;
return x;
}
//void myObj_assist(t_myObj *x, void *b, long m, long a, char *s) {
// if (m==1) {
// switch(a) {
// case 0: sprintf (s,"message inlet"); break;
// }
// }
// else {
// switch(a) {
// case 0: sprintf (s,"(signal) signal out osc1"); break;
// case 1: sprintf(s, "(signal) signal out osc2"); break;
// case 2: sprintf(s, "(signal) signal out osc3"); break;
// case 3: sprintf(s, "(signal) signal out osc4"); break;
// }
//
// }
//}
Abstraction list append and cold right inlet
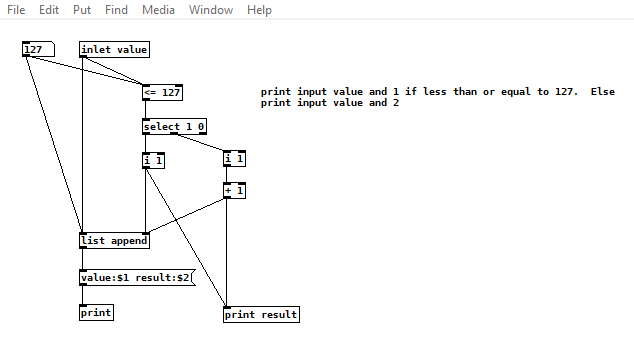
I am getting a different result in my code when I run a patch as a an abstraction vs on its own. The issue seems to be with a list append object and the right cold inlet. The patch does the following:
- takes a number input
- pass the number input to the hot side of the list append
- if the number input is <= 127, pass 1 to the right cold side of list append else if it is 128 or greater pass 1 + 1 (2) to the right cold side list append.
- format the list in a message, print the message
- and also print the value of the data directly.
Here is the abstraction patch:
Here is the main patch:
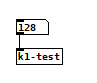
When I run the main patch and enter 127 then 128 into the number atom I get the following output in the console:
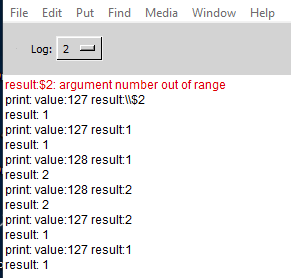
first problem is the number out of range. Second problem is that the $2 value in the message is not the same as the value printed from "print result".
When I run the patch on its own and use the number atom in the patch for the value I get a different output in the console:
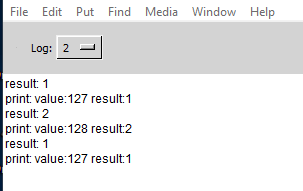
In this case the value of "print result" and the $2 value in the message are the same.
It seems there is a difference in the order of execution of the print statements and maybe there is also a difference in order of when the cold inlet on the list append gets updated.
Why is there a difference when run as an abstraction and how do I correct the number out of range error?
thanks for your help.
ofelia lua table and a few questions
second try. i commented out the lines where i am not sure if they are a methods (i am quite new to programming except for pure data and a little bit of python). there are only "public:" methods in the list.
class Canvas
// Canvas(t_symbol *s)
// Canvas(t_symbol *s, t_floatarg f)
t_symbol *realizeDollar(t_symbol *s)
t_symbol *getName()
int getIndex()
void getArgs(int *argcp, t_atom **argvp, t_canvas **canvasp)
void setArgs(int argc, t_atom *argv)
void getPosition(int **posp)
void setPosition(int xpos, int ypos)
t_symbol *getDir()
void remove()
class Send
// Send(t_symbol *s)
void sendBang()sendFloat(t_floatarg f)
void sendSymbol(t_symbol *s)
void sendPointer(t_gpointer *p)
void sendList(int argc, t_atom *argv)
void sendAnything(int argc, t_atom *argv)
class Inlet
// Inlet(t_symbol *s)
void setFloatInlet(t_floatarg f)
void setFloatInlets(int n, t_floatarg *f)
void setSignalInlet(t_floatarg f)
class Outlet
// Outlet(t_symbol *s)
void outletBang(int index)
void outletFloat(int index, t_floatarg f)
void outletSymbol(int index, t_symbol *s)
void outletPointer(int index, t_gpointer *p)
void outletList(int index, int argc, t_atom *argv)
void outletAnything(int index, int argc, t_atom *argv)
class Value
// Value(t_symbol *s)
virtual ~Value()
t_float get()
void set(t_floatarg f)
class Array
// Array(t_symbol *s)
bool exists(t_garray **a)
float getAt(int n)
float getAt(int n)
void getTable(t_word **vecp, int *sizep)
void setTable(int n, t_floatarg *f)
int getSize()
void setSize(long n)
class Clock
// Clock(t_symbol *s)
// Clock(t_symbol *s, t_symbol *s2)
virtual ~Clock()
void delay(double delayTime)
void unset()
class Sys
double getRealTime()
void lock()
void unlock()
int tryLock()
void gui(t_symbol *s)
class Signal
int getBlockSize()
t_float getSampleRate()
int getInChannels()
int getOutChannels()
bool getDspState()
class PD
int getMaxString()
int getFloatSize()
t_float getMinFloat()
t_float getMaxFloat()
bool isBadFloat(t_floatarg f)
bool isBigOrSmall(t_floatarg f)
tuple<int, int, int> getVersion()
// int maxString;
// int floatSize;
// t_float minFloat;
// t_float maxFloat;
// tuple<int, int, int> version;
class Log
void post(const char *s)
void post(const char *s, int level)
void startPost(const char *s)
void postString(const char *s)
void postFloat(t_floatarg f)
void postAtom(int argc, t_atom *argv)
void endPost()
void error(const char *s)
Table-using Abstraction can be used multiple times in one patch
@Maggie17 Sometimes it is easier with words........
Dollar $ variables in Pure Data patches.
A dollar variable is a thing that can be given a new value.
The new value can be a float or a symbol.
- If the Dollar variable is in an [object] box
A Pd patch can be saved and used inside another patch. We then call it an abstraction.... and it is just like a programming sub-routine.
If you want to use it many times then you have a problem, that they are all the same, so if you put an object [receive woof] they will all receive any message that you send with [send woof].
That might well be what you want to do.
But what if you want to send the message to only one of them?
You can give it an [inlet], but your patch will get messy, and what if your patch needs to make its own mind up about which abstraction it wants to send the message to, maybe depending on which midi note it received?
The solution is to give the abstraction arguments... some parameters that define it and make it different to the other copies.
For example [my_abstraction]
Let’s give it some arguments [my_abstraction 5 9 woof]
Inside the abstraction, as it is created (you open its parent patch) the dollar variables will be replaced. Wherever you see $1 written IN AN OBJECT it has been replaced by the number 5.
Number 5 because 5 is the first argument and has actually replaced the $1. You still see $1, but if you bang a [$1] object it will output 5.
[f $2] will output 9
[symbol $3] will output woof
So if you have an object [receive $1-$3] then it has now become [receive 5-woof]
And if you want to send it a message from outside, from another patch or abstraction, you will need to use [send 5-woof]
Every Pd patch, which remember includes your abstractions, also has a secret number. The number is unique and greater than 1000. As Pd opens each patch it gives it the number, increased by one from the last number it gave.
That number will replace $0 as the patch is created. You can find out what the number is by banging a [$0] object and connecting its output to a number box, or [print] object.
$0 can be used in any object as part of the name or the address, which means that a message cannot escape from the abstraction. A sub-patch like [pd my-subpatch] will be given the same number.
But from outside your abstraction you don’t know what it will be when the patch is created, so it is not useful. (A lie, you can find out, but as it can change every time you open your patch it is not worth the bother).
Use it to send messages within your patch [send $0-reset] to [receive $0-reset] for example, because the message is absolutely unique to its window, so you know it cannot interfere with other abstractions. - If the Dollar $ variable in a [message( box
Dollar $ variables are also replaced, but not as the patch is created (drawn by Pd as you open it).
Dollar zero $0 has no meaning in a message box. It will produce a zero if the message is banged, but that is it.
It is a mistake, a patching error, to put a $0 in a message box.
$1 $2 $3 $4 etc. in a message box are replaced by incoming atoms (individual floats or symbols or whatever) when they arrive. $1 will be replaced by the first atom in the list, $2 the second etc.
So if you have a message box [$1 $2 $3( ..... and you send into it a list [3 48 lala( .....then it will output 3 48 lala
That is not really very useful.
But it is actually very powerful.
Make a list in a message box........ [33 12 wav(
And bang it into a message box [open my-track$2-$1.$3( and you will get the output.........
open my-track12-33.wav
Which could be just the message that you want to send to [soundfiler]
David.
ofelia lua table and a few questions
@cuinjune i took a look into ofeliaBindings.h and i tried to make a list of the classes and methods that call internal pd methods.
i am not sure if it is correct / complete but at least it is an orientation for me.
class Canvas
int getIndex()
void getArgs(int *argcp, t_atom **argvp, t_canvas **canvasp)
void setArgs(int argc, t_atom *argv)
void getPosition(int **posp)
void setPosition(int xpos, int ypos)
void remove()
class Send
void sendBang()sendFloat(t_floatarg f)
void sendSymbol(t_symbol *s)
void sendPointer(t_gpointer *p)
void sendList(int argc, t_atom *argv)
void sendAnything(int argc, t_atom *argv)
class Inlet
void setFloatInlet(t_floatarg f)
void setFloatInlets(int n, t_floatarg *f)
void setSignalInlet(t_floatarg f)
class Outlet
void outletBang(int index)
void outletFloat(int index, t_floatarg f)
void outletSymbol(int index, t_symbol *s)
void outletPointer(int index, t_gpointer *p)
void outletList(int index, int argc, t_atom *argv)
void outletAnything(int index, int argc, t_atom *argv)
class Value
void set(t_floatarg f)
class Array
float getAt(int n)
float getAt(int n)
void getTable(t_word **vecp, int *sizep)
void setTable(int n, t_floatarg *f)
int getSize()
void setSize(long n)
class Clock
void delay(double delayTime)
void unset()
class Sys
double getRealTime()
void lock()
void unlock()
int tryLock()
void gui(t_symbol *s)
class PD
int getMaxString()
int getFloatSize()
t_float getMinFloat()
t_float getMaxFloat()
bool isBadFloat(t_floatarg f)
bool isBigOrSmall(t_floatarg f)
tuple<int, int, int> getVersion()
Closing patches without Pd crashing, hopefully in an elegant way...
@whale-av Yes, the first patch closes fine, but the 2nd patch that closes it is crashing Pd.
I was thinking of another possibility. I could have 3 patches, and one just stays open the whole time, which would be the patch that closes all the other patches.
I would open my first patch. My 2nd patch would be the one that I would use to perform. Then when I want to change patches for a performance I open the 3rd patch that sends some kind of trigger that the 1st patch uses to close the 2nd patch, and then it closes the 3rd patch. The 1st patch just stays open till I shutdown.
It's a convoluted scheme, but that way I can avoid a patch needing to closes itself, which I think is what the problem is.
Closing patches without Pd crashing, hopefully in an elegant way...
Hi,
I have a headless Rpi setup using Pd .49.
I am trying to have everything automated, and one thing I'm trying to work out is that I want to close the patch I'm using before I open the next patch. I am doing this by sending internal Pd messages.
I used to quit Pd and re-open it, but due to problems I couldn't resolve after much time connecting my midi controller, I am going to try to just close my patch rather than quit and reopen Pd.
What I've worked out is that every patch will have a [r closepatch] object, and when I want to change patches I will open a patch that will send a bang from [s closepatch] , then it will close itself. I added several seconds of delay time to both patches, but this method always causes Pd to crash.
I am using this message to close a patch: [; pd-mypatch.pd menuclose 1(
My question: How can I close a patch from another patch, and then close the patch that closed the first one? Or is there a better way.
Even better, is there a way that I don't have to enter in the name of the main patch I want to close, like can I use some sort of variable, or send another internal message that will load the patch name into the patch closing message?
I am attatching what I have. First open "closetest1.pd" then "close_patch5.pd" If you connect the messages you can test them properly, but they always make Pd crash on my Rpi.
Thank You.