foo_pd - Pure Data plugin for foobar2000
This is a spiritual successor to amPd. It's much more stable and has many more features than amPd:
-
reads/writes metadata to/from patches. This is done by storing the info in the form of comments, in a canvas called [pd meta] or [pd info]. If no such canvas exists, foobar will add it in the top left-hand corner of your patch.
-
comes with a Win32 Dialog UI element, containing sliders, toggles, buttons, and edit-text/button combos to send messages to your patch.
- foobar looks in your patch for a canvas called [pd mix] and uses the parameters of whatever sliders, bang objects, or toggles it finds there to give your UI controls similar functionality.
How playback works
- libpd sends a 1 to vol, then a bang to play.
- Generally this is where, in your patch, you have an [r play] hooked up to your metro, and an [r vol] connected to a [*~ ] before your output reaches [dac~].
- the length of the song is arbitrarily set by the user.
- This affects the trackbar's cursor visibility and ability to set a position.
- If the length is 0, there will be no trackbar cursor. Otherwise, the cursor, when moved, will send its position in seconds to pos. From there, it's up to your patch to take that information from [r pos] and work it into song events.
- The patch will not actually stop and move on to the next track until libpd receives a bang from [s stop].
How the mixer works
- all mixer controls go inside of [pd mix]
- horizontal and vertical sliders are turned into slider controls in the UI element
- labels assigned to sliders in the patch become labels for the UI element's slider controls. The same applies for send symbols.
- min and max values of sliders on the UI element work in integers only, so if you want a gradual shift from, say, 0 to 1, write "gradient" in the slider's receive symbol, and the slider's range will be broken down into roughly 200+ individual steps.
- there are currently 7 sliders in the UI element
- bang objects with no label become simple buttons in the UI
- their send symbols will be reflected in the button's name and they will send a bang when clicked.
- there are currently 3 buttons
- bang objects with a label assigned become message buttons
- these have an edit text field associated with them, where you can type out any message you want and send it to the destination.
- the bang's label is placed inside of the edit text field as a suggested message to send.
- pure data strips commas out of labels, so I'm using apostrophes to denote where commas should go. ex: do this' then this
- there are currently 2 message buttons, with the 'any' button being a potential 3rd.
- a bang object with a label written in the format dest : msg will be assigned to the 'any' button.
- the 'any' button has an editable destination field, giving you access to basically any receive symbol in your patch.
- also substitutes as a third normal message button, when the other two are already in use
- toggles become checkboxes
- each checkbox can have a label and send symbol assigned to it
- there are currently 4 checkboxes
- right-clicking a track shows the context menu entry Pd Player -> Load mixer.
- basically, you can load mixers of tracks not currently playing for some potentially interesting exchanges between patches. After loading the mixer, you still need to hit the Refresh button to show the changes.
foo_pd's copy of libpd.dll contains only the externals that I needed to run the example patches. If you want your own patches to work with foo_pd, you might need to make another build using MSYS2. If you're not sure which objects aren't instantiating, foobar's console prints all of pd's messages while audio is being processed. I'll also add more externals over time.
I'll be maintaining foo_pd at https://github.com/myQwil/foo_pd where you can also find the latest builds
foo_pd.zip
Last Updated: Feb 26, 2021 3:55pm EST
TimbreID On Raspberry Pi
Compiling only TimbreId against pd (not compiling pd source).
To load timbreIDLib, list the path to the timbreIDLib library file in Pd's startup dialog (e.g., /home/yourname/pd_libs/timbreID/timbreIDLib).
timbreID version 0.7 requires the FFTW library, available at http://www.fftw.org.
FFTW is included pre-compiled with timbreID's Windows binary package available through deken. It's fine to simply leave libfftw3f-3.dll in the timbreID directory for use as a shared library. For Linux and Macintosh, FFTW is statically linked with the timbreIDLib library file, so there is no need for compiling or obtaining FFTW.
If you are compliling FFTW yourself, it must be compiled in single precision. To do so in Linux, configure FFTW like this:
./configure CFLAGS="-fPIC" --enable-float
and like this on a Macintosh:
./configure CFLAGS="-arch i386 -arch x86_64" --enable-float
Then run:
make
sudo make install
The FFTW library for Windows is available precompiled at:
http://www.fftw.org/install/windows.html
You will need the 32-bit version, and the single precision version specifically. The provided zip file contains several compiled versions of FFTW, but only libfftw3f-3.dll is required for timbreID version 0.7.
On Linux and Macintosh, the FFTW library files should be installed to /usr/local/lib by default. Once FFTW is properly built and installed, you can make timbreID using the included Makefile by running:
make
You must specify the location of your Pure Data source code directory in the Makefile beforehand. Compilation from source on Windows can be done with the same Makefile if you use MinGW: http://www.mingw.org
On Linux and Macintosh, timbreIDLib will statically link the FFTW library. On Windows, you will either have to set up an environment variable to point to the location of libfftw3f-3.dll, or simply put libfftw3f-3.dll directly in the timbreID directory.
Cheers~
Playing sound files based on numbers/sets of numbers?
@whale-av Hello, first I just want to say thank you very much for your help and sorry for not replying sooner, I read all the messages, I just didn't want to bother people before I had an actual issue or a question that I understood enough to know how to ask what to do next. So that's why I'm only replying now. And you're totally right, I have suffered and learned in the past day so my brain's kind of all over the place right now, I'm still struggling to get the hang of this and really understand the patches you sent me (thank you so much for taking the time to make them for me!).
To answer your questions, I will not be assessed for this part of the project, it doesn't matter much how I do it as long as it works because no one will look at the project anyway, the end result is what matters in this case. The only "limitation" is that it has to be done in Pd. Also, my version of Pd is Vanilla (I'm assuming that doesn't change your patch much since you said it'd work in that version), and actually no, there's not really a next stage to this project; all I'm supposed to do is get my sound files to play in a loop when I press Enter (after I've typed all my numbers) and to be able to stop the loop again with Enter. I probably should have mentioned that oops, does that mean I need another keyup object or would the one in the patch work for both starting and stopping the sound?
I actually had a patch of my own but it was very simple and mostly improvised based on what I managed to learn (like I said, completely new to this) and nothing like yours so it probably wouldn't have worked anyway... Is it ok if I use your patch as a starting point? If it is, I'm assuming the next step would be the abstractions. From what I understand, abstractions are used for referencing and reusing old patches in order to keep the new patch clean and not messy. I do need something like that, as I have 17 wav files ready to use. But not all 17 should be used in one loop. I actually only need 5 sound files per loop (like in your patch), but the total number of files I can choose from is 17. To be able to tell the program which file to play based on its corresponding number I probably need the select object, right? Would I need it within the calling patch or the patch being called, a.k.a. abstraction (if my thinking is right, it's probably the calling patch)? There's probably an easier way to do this than an x number of select objects but I'm just not familiar enough with the program, sorry... Also, what difference does it make if it's not 1-digit numbers, but 2-digit, 3-digit and 4-digit combinations? To be more precise, the first, second and fourth sound file should correspond to a 2-digit number, the third to a 3-digit number, and the fifth to a 4-digit number (and I can't change this unfortunately, it's part of the task).
Oh, and is there a way I can make this work on any computer, for example if I copy my files onto a flash drive? Or if I can't, would it drastically affect my main patch if I changed the sound file destinations later, once I know what computer is going to be doing all this? Would I need to change the file destinations in all the patches or would it be possible to do so automatically via abstractions, by changing them in the main patch only (probably not but eh I asked...)?
This is all probably waaay too advanced for a beginner (and I have no idea why they'd give me this task without any prior preparation.......) so I realize I might be asking for too much here, and maybe I'm getting ahead of myself, but I still hope you could give some advice on what to do from here, what's the next step, the elements I need to get this done etc. I'm not in too much hurry, I have time until the 5th of February, so it's ok if you don't have the time for me right now, I can wait a bit!
Thank you so so so much, even just sending me the first patch was such a huge help, thank you! And I hope you can guide me through this for a bit longer!
Pure Data noob
Ok...... So I have been meaning to do this for a very long time......
I don't think it is the perfect "show_me_dollars" and so I will change it from time to time.
3rd attempt.........
show_me_dollars.zip
Here is a really terrifying screenshot, but I have also tried to explain it in words.
In many ways I think words ( below the screenshot) are easier to understand.
David.
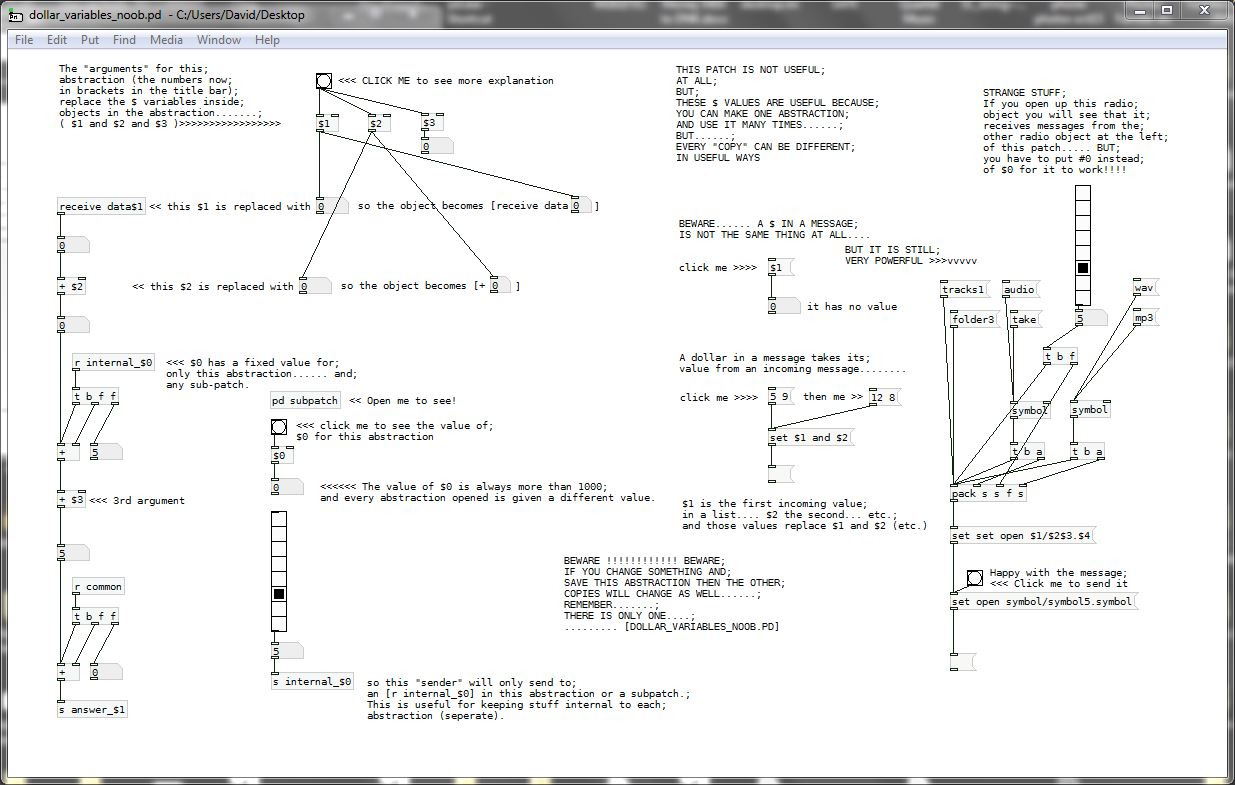
Dollar $ variables in Pure Data patches.
A dollar variable is a thing that can be given a new value.
The new value can be a float or a symbol.
- If the Dollar variable is in an [object] box
A Pd patch can be saved and used inside another patch. We then call it an abstraction.... and it is just like a programming sub-routine.
If you want to use it many times then you have a problem, that they are all the same, so if you put an object [receive woof] they will all receive any message that you send with [send woof].
That might well be what you want to do.
But what if you want to send the message to only one of them?
You can give it an [inlet], but your patch will get messy, and what if your patch needs to make its own mind up about which abstraction it wants to send the message to, maybe depending on which midi note it received?
The solution is to give the abstraction arguments... some parameters that define it and make it different to the other copies.
For example [my_abstraction]
Let’s give it some arguments [my_abstraction 5 9 woof]
Inside the abstraction, as it is created (you open its parent patch) the dollar variables will be replaced. Wherever you see $1 written IN AN OBJECT it has been replaced by the number 5.
Number 5 because 5 is the first argument and has actually replaced the $1. You still see $1, but if you bang a [$1] object it will output 5.
[f $2] will output 9
[symbol $3] will output woof
So if you have an object [receive $1-$3] then it has now become [receive 5-woof]
And if you want to send it a message from outside, from another patch or abstraction, you will need to use [send 5-woof]
Every Pd patch, which remember includes your abstractions, also has a secret number. The number is unique and greater than 1000. As Pd opens each patch it gives it the number, increased by one from the last number it gave.
That number will replace $0 as the patch is created. You can find out what the number is by banging a [$0] object and connecting its output to a number box, or [print] object.
$0 can be used in any object as part of the name or the address, which means that a message cannot escape from the abstraction. A sub-patch like [pd my-subpatch] will be given the same number.
But from outside your abstraction you don’t know what it will be when the patch is created, so it is not useful. (A lie, you can find out, but as it can change every time you open your patch it is not worth the bother).
Use it to send messages within your patch [send $0-reset] to [receive $0-reset] for example, because the message is absolutely unique to its window, so you know it cannot interfere with other abstractions.
Use it also for objects like [delwrite~ $0-buffer 100] or for an array name [array $0-array] so that in each abstraction they have a different name and you will not have problems with their being "multiply defined"...... as each name can only exist once in your patch.
- If the Dollar $ variable is in a [message( box
Dollar $ variables are also replaced, but not as the patch is created (drawn by Pd as you open it).
Dollar zero $0 has no meaning in a message box. It will produce a zero if the message is banged, but that is it.
It is a mistake, a patching error, to put a $0 in a message box.
$1 $2 $3 $4 etc. in a message box are replaced by incoming atoms (individual floats or symbols or whatever) when they arrive. $1 will be replaced by the first atom in the list, $2 the second etc.
So if you have a message box [$1 $2 $3( ..... and you send into it a list [3 48 lala( .....then it will output 3 48 lala
That is not really very useful.
But it is actually very powerful.
Make a list in a message box........ [33 12 wav(
And bang it into a message box [open my-track$2-$1.$3( and you will get the output.........
open my-track12-33.wav
Which could be just the message that you want to send to [soundfiler]
P.S. If the first item in the incoming list is a symbol then it will be dropped causing errors.
You can fix that by making the message a list by passing it through the object [list].
Unfortunately only messages starting with a float are automatically recognised as lists.
libpd on mac: clarification requested on expected behavior of cpp sample
Thanks for those links Monetus. I'm pretty close with my existing setup and will first try to work with that when I have some more time. Some of the output from the samples/cpp/pdtest appears to be as expected.
However, from main.cpp
cout << endl << "BEGIN Patch Test" << endl;
// open patch
Patch patch = pd.openPatch("pd/test.pd", ".");
cout << patch << endl;
// close patch
pd.closePatch(patch);
cout << patch << endl;
// open patch again
patch = pd.openPatch(patch);
cout << patch << endl;
// process any received messages
//
// in a normal case (not a test like this), you would call this in
// your application main loop
pd.processFloat(1, inbuf, outbuf);
pd.receiveMessages();
cout << "FINISH Patch Test" << endl;
the response
BEGIN Patch Test
Patch: "pd/test.pd" $0: 1003 valid: 1
Patch: "pd/test.pd" $0: 0 valid: 0
Patch: "pd/test.pd" $0: 1005 valid: 1
PD: PATCH OPENED: 1003
print: 0
PD: PATCH OPENED: 1005
print: 0
FINISH Patch Test
seems right but no patch was opened and if I already opened that patch before running the executable, none of the print messages (called later in the code) showed up in the console of pd. I'll focus on this and try to repost to the forum when I have a better idea of what is going on.
Loading a pure data patch ( .pd file ) within a pure data patch ( .pd file )
HI!
Quick version:
My folder structure:
/mother-patch.pd ( main pure data patch first loaded and running... )
/patches/1/main.pd
/patches/2/main.pd
/patches/3/main.pd
...
How i could open /patches/1/main.pd triggered by some action in the mother-patch.pd?
How i could close /patches/1/main.pd triggered by some action in the mother-patch.pd?
Long read
I'm attempting to clone the Critter and Guitari organelle ( link ).
This instrument is basically a computer running libpd and running very cool pure data patches
You can read more about my project here ( link )
I have a mother pure data patch that it's first loaded when the device is on, this patch is doing some [send] and [receive] operations related to the knobs/keyboard/volume/led and it should be also managing the loading ( opening and closing ) of the child pure data patches ( mentioned above ). This child patches are receiving the actions from the mother patch.
If I open the mother patch and the child patches manually, everything works fine. But now I need to OPEN this CHILD PURE DATA patches with a object within the mother patch.
I've been testing [open] , for opening the main.pd of the child patches but it does not work.
I've been testing [pd] , for opening the main.pd of the child patches but it does not work.
I wouldn't like to modify the original organelle patches.
I wouldn't like to end up loading all the patches using [pd ...] and inserting a [switch] object inside every main.pd file in the patches in order to enable only the dsp of the desired patch.
It would be perfect If i could have a folder with all the patches and load them within the mother patch with some kind of object. And I would also want to be able to CLOSE the pure data patch and open another ( changing patches... )
Every little and big help woul be MUCH APRECIATED!
THANKS!!!!!!!
New to PD, need help with notes failing to turn off.
I've been working on my first major patch for the past few months. It's a synthesizer based heavily on the tutorial on flossmanuals.net. After finally creating all of the features I wanted I started to modify the patch to make the synthesizer polyphonic. The catch is that I want to control the patch using the Mad Catz Mustang midi guitar controller. This controller works perfectly fine with the polyphonic synth in the PD help browser as well as with other polyphonic synth patches I've found online, so I do not think the controller has any problem interacting with the [poly] object.. The problem is that when I use it with my patch, some notes fail to turn off. It seems to happen most often when I quickly slur from one note to another. I did not have this issue when using the monophonic version of my patch. The amplifier subpatch is definitely receiving noteoff messages, but for some reason, they do not cause the envelope to close.
I think part of the problem has to do with the way the controller sends messages. I use the controller in 'tap mode,' meaning a noteon is sent whenever a fret button is pressed and noteoffs are sent when fret buttons are released. However noteoffs are also sent whenever any fret button is pressed in order to turn off the "open string" (A note can be played without pressing a fret button by striking the string sensors, and the only way to turn it off is by playing a fretted note). This occurs whether or not the open string is playing and I think this may be messing with [poly]'s voice allocation. I'm tempted to just say that the controller can't be worked around, but since I know it works for other patches I'm going crazy trying to fix my patch.
I understand it would be hard to duplicate this behavior without having the controller, but as I said before it works like a dream with other patches. I have tried to imitate the polyphony of these patches as best as I can. I've tried disconnecting and reconnecting objects in every order imaginable and I've tried delaying on and off messages in case they were somehow arriving to the amplifier envelope out of order.
Attached is a simplified version of my polyph[full poly help.pd] onic patch. I'd really appreciate it if anyone could give it a quick look over just in case there's anything really obvious that I'm just missing.
Thanks so much and have a great day.
EDIT: Please ignore the errors about missing {receive~}s or {catch~}es. The {send~}s and {throw~}s are for some of the features that I removed from this version of the patch for simplicity's sake but I did not remove the {send~}s and {throw~}s.
use of threads for i²c I/O external : looking for a good strategy
@nau Hi, same boat (I don't know much about Pd internal functions & pthread), but maybe you can try to see if this external (really similar to my template, but this time to fetch real data for my HiCu project).
Look for m_clock / m_interval and clock_delay.
// ==============================================================================
// gac.c
//
// pd-Interface to [ 11h11 | gac ]
// Adapted by: Patrick Sebastien Coulombe
// Website: http://www.workinprogress.ca/guitare-a-crayon
//
// Original Author: Michael Egger
// Copyright: 2007 [ a n y m a ]
// Website: http://gnusb.sourceforge.net/
//
// License: GNU GPL 2.0 www.gnu.org
// Version: 2009-04-11
// ==============================================================================
// ==============================================================================
#include "m_pd.h"
#include <usb.h> //http://libusb-win32.sourceforge.net
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "pthread.h"
#include "../common/gac_cmds.h"
// ==============================================================================
// Constants
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define USBDEV_SHARED_VENDOR 0x16c0 /* VOTI */
#define USBDEV_SHARED_PRODUCT 0x05dc /* Obdev's free shared PID */
#define DEFAULT_CLOCK_INTERVAL 34 /* ms */
#define OUTLETS 11
#define USBREPLYBUFFER 14
unsigned char buffer[USBREPLYBUFFER]; //accessible everywhere
// ==============================================================================
// Our External's Memory structure
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
typedef struct _gac // defines our object's internal variables for each instance in a patch
{
t_object p_ob; // object header - ALL pd external MUST begin with this...
usb_dev_handle *dev_handle; // handle to the gac usb device
void *m_clock; // handle to our clock
double m_interval; // clock interval for polling edubeat
double m_interval_bak; // backup clock interval for polling edubeat
int is_running; // is our clock ticking?
void *outlets[OUTLETS]; // handle to the objects outlets
int x_verbose;
pthread_attr_t gac_thread_attr;
pthread_t x_threadid;
} t_gac;
void *gac_class; // global pointer to the object class - so pd can reference the object
// ==============================================================================
// Function Prototypes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void *gac_new(t_symbol *s);
void gac_assist(t_gac *x, void *b, long m, long a, char *s);
void gac_bang(t_gac *x);
void gac_bootloader(t_gac *x);
static int usbGetStringAscii(usb_dev_handle *dev, int ndex, int langid, char *buf, int buflen);
void find_device(t_gac *x);
// =============================================================================
// Threading
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void *usb_thread_read(void *w)
{
t_gac *x = (t_gac*) w;
int nBytes;
while(1) {
pthread_testcancel();
if (!(x->dev_handle)) find_device(x);
else {
nBytes = usb_control_msg(x->dev_handle, USB_TYPE_VENDOR | USB_RECIP_DEVICE | USB_ENDPOINT_IN,
EDUBEAT_CMD_POLL, 0, 0, (char *)buffer, sizeof(buffer), DEFAULT_CLOCK_INTERVAL);
if(x->x_verbose)post("thread read %i bytes", nBytes);
//post("%i b", nBytes);
}
}
return 0;
}
static void usb_thread_start(t_gac *x) {
// create the worker thread
if(pthread_attr_init(&x->gac_thread_attr) < 0)
{
error("gac: could not launch receive thread");
return;
}
if(pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&x->gac_thread_attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED) < 0)
{
error("gac: could not launch receive thread");
return;
}
if(pthread_create(&x->x_threadid, &x->gac_thread_attr, usb_thread_read, x) < 0)
{
error("gac: could not launch receive thread");
return;
}
else
{
if(x->x_verbose)post("gac: thread %d launched", (int)x->x_threadid );
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - Message: bootloader
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
void gac_bootloader(t_gac *x)
{
int cmd;
int nBytes;
unsigned char bootloaderbuffer[8];
cmd = 0;
cmd = EDUBEAT_CMD_START_BOOTLOADER;
if (!(x->dev_handle)) find_device(x);
else {
nBytes = usb_control_msg(x->dev_handle, USB_TYPE_VENDOR | USB_RECIP_DEVICE | USB_ENDPOINT_IN,
cmd, 0, 0, (char *)bootloaderbuffer, sizeof(bootloaderbuffer), DEFAULT_CLOCK_INTERVAL);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - Message: bang -> poll gac
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
void gac_bang(t_gac *x) {
int i,n;
int replymask,replyshift,replybyte;
int temp;
for (i = 0; i < OUTLETS; i++) {
temp = buffer[i];
switch(i) {
case 0:
replybyte = buffer[8];
replyshift = ((0 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 1:
replybyte = buffer[8];
replyshift = ((1 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 2:
replybyte = buffer[8];
replyshift = ((2 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 3:
replybyte = buffer[8];
replyshift = ((3 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 4:
replybyte = buffer[9];
replyshift = ((0 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 5:
replybyte = buffer[9];
replyshift = ((1 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 6:
replybyte = buffer[9];
replyshift = ((2 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 8:
temp = buffer[10];
replybyte = buffer[13];
replyshift = ((0 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 9:
temp = buffer[11];
replybyte = buffer[13];
replyshift = ((1 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
case 10:
temp = buffer[12];
replybyte = buffer[13];
replyshift = ((2 % 4) * 2);
replymask = (3 << replyshift);
temp = temp * 4 + ((replybyte & replymask) >> replyshift);
break;
}
outlet_float(x->outlets[i], temp);
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - The clock is ticking, tic, tac...
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
void gac_tick(t_gac *x) {
clock_delay(x->m_clock, x->m_interval); // schedule another tick
gac_bang(x); // poll the edubeat
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - Object creation and setup
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
int gac_setup(void)
{
gac_class = class_new ( gensym("gac"),(t_newmethod)gac_new, 0, sizeof(t_gac), CLASS_DEFAULT,0);
// Add message handlers
class_addbang(gac_class, (t_method)gac_bang);
class_addmethod(gac_class, (t_method)gac_bootloader, gensym("bootloader"), A_DEFSYM,0);
post("bald-approved gac version 0.1",0);
return 1;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
void *gac_new(t_symbol *s) // s = optional argument typed into object box (A_SYM) -- defaults to 0 if no args are typed
{
t_gac *x; // local variable (pointer to a t_gac data structure)
x = (t_gac *)pd_new(gac_class); // create a new instance of this object
x->m_clock = clock_new(x,(t_method)gac_tick);
x->x_verbose = 0;
x->m_interval = DEFAULT_CLOCK_INTERVAL;
x->m_interval_bak = DEFAULT_CLOCK_INTERVAL;
x->dev_handle = NULL;
int i;
// create outlets and assign it to our outlet variable in the instance's data structure
for (i=0; i < OUTLETS; i++) {
x->outlets[i] = outlet_new(&x->p_ob, &s_float);
}
usb_thread_start(x); //start polling the device
clock_delay(x->m_clock,0.); //start reading the buffer
return x; // return a reference to the object instance
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - Object destruction
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
void gac_free(t_gac *x)
{
if (x->dev_handle) usb_close(x->dev_handle);
freebytes((t_object *)x->m_clock, sizeof(x->m_clock));
while(pthread_cancel(x->x_threadid) < 0)
if(x->x_verbose)post("gac: killing thread\n");
if(x->x_verbose)post("gac: thread canceled\n");
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - USB Utility Functions
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
static int usbGetStringAscii(usb_dev_handle *dev, int ndex, int langid, char *buf, int buflen)
{
char asciibuffer[256];
int rval, i;
if((rval = usb_control_msg(dev, USB_ENDPOINT_IN, USB_REQ_GET_DESCRIPTOR, (USB_DT_STRING << 8) + ndex, langid, asciibuffer, sizeof(asciibuffer), 1000)) < 0)
return rval;
if(asciibuffer[1] != USB_DT_STRING)
return 0;
if((unsigned char)asciibuffer[0] < rval)
rval = (unsigned char)asciibuffer[0];
rval /= 2;
/* lossy conversion to ISO Latin1 */
for(i=1;i<rval;i++){
if(i > buflen) /* destination buffer overflow */
break;
buf[i-1] = asciibuffer[2 * i];
if(asciibuffer[2 * i + 1] != 0) /* outside of ISO Latin1 range */
buf[i-1] = '?';
}
buf[i-1] = 0;
return i-1;
}
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------
void find_device(t_gac *x) {
usb_dev_handle *handle = NULL;
struct usb_bus *bus;
struct usb_device *dev;
usb_init();
usb_find_busses();
usb_find_devices();
for(bus=usb_busses; bus; bus=bus->next){
for(dev=bus->devices; dev; dev=dev->next){
if(dev->descriptor.idVendor == USBDEV_SHARED_VENDOR && dev->descriptor.idProduct == USBDEV_SHARED_PRODUCT){
char string[256];
int len;
handle = usb_open(dev); /* we need to open the device in order to query strings */
if(!handle){
error ("Warning: cannot open USB device: %s", usb_strerror());
continue;
}
/* now find out whether the device actually is gac */
len = usbGetStringAscii(handle, dev->descriptor.iManufacturer, 0x0409, string, sizeof(string));
if(len < 0){
post("gac: warning: cannot query manufacturer for device: %s", usb_strerror());
goto skipDevice;
}
post("::::::%s", string);
if(strcmp(string, "11h11") != 0)
goto skipDevice;
len = usbGetStringAscii(handle, dev->descriptor.iProduct, 0x0409, string, sizeof(string));
if(len < 0){
post("gac: warning: cannot query product for device: %s", usb_strerror());
goto skipDevice;
}
if(strcmp(string, "Gac") == 0)
break;
skipDevice:
usb_close(handle);
handle = NULL;
}
}
if(handle)
break;
}
if(!handle){
post("Could not find USB device 11h11/gac");
x->dev_handle = NULL;
} else {
x->dev_handle = handle;
post("Found USB device 11h11/gac");
}
}
Cheers
Export to exe or dmg format
Eimer,
Pd and Pd-extended is free software and you may redistribute it, even in modified form, provided you follow the license terms (BSD and GPL).
If you are on OSX, it is very easy to create your own application with Pd-extended under the hood. Select menu-item 'file>>Make app from patch' or 'file>>Make app from folder'. What you get is a Pd-extended package with your patch as startup patch. The Pd window is minimized directly after startup, so at a first glance you don't notice it is Pd. But it is still fully functional with all Pd-extended libraries in it (120 MB!), and the possibility to edit patches and create new ones. With some extra tweaking, you can replace the Pd icon with an icon of your own make. The preferences file of this 'app' is within the app folder. If you included all necessary abstractions, and eventually your homebrew externals, you can distribute it as a stand alone app.
But probably you are not on OSX, otherwise you would have already seen this option. For Linux or Windows you could do something similar to the 'Make app' as described above, but do it by hand. You could write an executable tcl script to start Pd with your patch as startup patch, and eventually include other options in the script. (Pd uses Tk/tcl for graphics and other purposes, so it is included in every binary distribution of Pd-extended). The user can click that script to open your 'application'.
Disadvantages of distributing apps instead of patches are:
- you need to make separate distributions for every platform
- applications are large so you need ample download bandwidth on your server or host
- if Pd is obscured, you can't refer to Pd pages for support
All taken together, I see little advantage for distributing stand alone apps rather than Pd patches. If you want to make user-friendly distributions of your patches, you could organise them in a decent directory structure, where abstractions and other essential files are included in the search path by the [declare] object. For the user it is then a matter of installing a recent Pd(-extended) if they do not have it yet, and opening the main patch in your patches package. If all goes well, this is piece of cake, and on the other hand if they have troubles with soundcards etcetera, this is not something you could have prevented by supplying an app instead of a patch.
Katja
Open Kinect?
hey buscon,
here's a copy of a mail i sent a friend, and the corresponding patches.
you can see these patches being used here:
(original mail)
ok here's a simplified version of the patch i use. i've just modified the "mud" patch and haven't checked it all, so there are bugs and errors everywhere, but i guess you're just interested in the abs which receive and dispatch the data from kinect.
so the kinect is received by osceleton and what i get in pd is osc messages. basically it's x, y, and z coordinates for each point of the body. so you'll be interested in the patches "kinector" and "shooter".
KINECTOR:
- it translates the osc into data that the granular sampler "mud" can understand (0 to 1 linear).
- move the horizontal sliders to chose a user and a joint.
- toggle from "value" to "CC". in X Y and Z type a sending chanel number. in the granular patch, toggle from value to CC, so you can affect a receiving chanel number for each automatisable parameter.
- hit the "learn" buton and then cover with your body the area you wish to use. this sets minimums and maximum for each axis. if you want to calibrate the whole body at ounce first select "all_joints". hit the "learn" buton again to end calibration. body motion is now active.
- the toggle on the top right activates remote sound control for the "learn" function, for if you work alone. enable it, use the vertical slider to choose the gate for incoming volume. stand at your starting point, and clap or scream. calibrate, and clap again.
- if you toggle from "abs" to "rltv", instead of calibrating the movement of each joint in absolute space it will consider their relative distance to the torso joint. the advantage of this is one movement will have the same effect wherever you are positioned in the space.
- you save, open, and load presets as textfiles on your drive. you can save presets for the whole patch on the top right of the master patch.
SHOOTER:
- basically the same as kinector, but used for one-shots instead of continuous changes.
- chose a user, a joint, an axis, and a direction
- type a chanel cumber where it says CC
- in "time", type a time in miliseconds. everytime a joint passes a chosen point in space in a chosen direction, it will output a line from 0 to 1 in the chosen time.
- calibrate in the same way. you can use "all_joints" too bu there's a huge error somewhere so if you do first toggle to "value".
- same as kinector for the rest.
ok here you go. i don't know how much you know pd, so that's why i explained as much as i could. these patches are absolutely not clean, they're my first ideas since i got the kinect, and i'm working on more to have one tight patch in the end (including speed detection, movement prevision to compensate latency, etc ... ).
ok hope this helps.
if you have trouble using the "mud" patch let me know. if you are going to use the patch, please let me know and make sure you mention it's mine.
cheers
salut
gab



