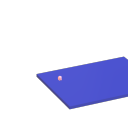
Starting up problem.
@beem Yes, you cannot rename main.pd........ it's the folder that can be renamed.
@JackOats No. In edit mode drag across the [declare -path patch_editor_abs] with the mouse to select it and then copy it and paste it within the main.pd window before editing it.
If @beem has not solved the problem for you then.........
Let's try something else. Trying to find what is going on.
On your screenshot were a lot of the modules named in red and marked couldn't create.
Choose one, say basic-osc.
In main.pd click on the file menu and then "Put" "Object" and then type basic-osc into the object.
Does it create?....... pop up as a bigger window with the oscillator in it?
No?
Go into the patch_editor_abs folder and copy basic-osc.pd and paste it into the Pd/bin folder, or into the "extra" folder if there is one (the one that contains the ggee folder).
Back to main.pd and try putting the object basic-osc again.
No?
Yes?
If it does then try the module button for basic-osc.
Does it now work?
No?
Copy main.pd into the patch_editor_abs folder..... open it..... and try the first step again (put, object, basic-osc).
If none of that works then I think it must be a security permissions problem.
David.
PdParty, sending/recieving OSC
Hi folks!
I reached this thread because I had the same problem: there were no way to receive OSC messages in PDparty. I was sending a simple bang from Isadora, just for test purposes, and it works fine on PD on my Mac (sending to locahost), but does not work sending to my Iphone IP. I was sure that the OSC were issued corrected, cause I can see them on Isadora OSC monitor.
Finally I found the problem was a conflict between the OSC incoming port in PDparty (Iphone) and de OSC port that the patch is lisent to (specified in a message to netreceive). If this one (in netreceive) is the same that the one in Port incoming (PDparty), you get in the console this error "error: blind: Address already in use (48), and the patch in PDparty do not receive OSC messages. I changed the OSC incoming port in PD settings, and the patch is receiving OSC messages to the port specified in [lisent] and [netreceive].
I attach my test patch (just play the sound file "cascabel" from the bang button or from OSC (send "/toggle1 1" to port 4321 to the IP where PDparty is running).
Hope it is useful for somebody. I was stuck for hours finding the reason for no receiving OSC
Regards
Daniel
TEST_PDparty.pd cascabel.wav
DC-Offset sound without DC-Offset?
@s.elliot.perez said:
Hey, I'm distorting and filtering some noise to get very low-pitched sounds. I want the high-pitched hum that comes with DC-offset (it gets better when I deliberately add a [+~ 0.5]), but I've read that DC-offset can be harmful to equipment. Does this hold true when done in Pure Data as well? If so, any tips on getting the DC-offset "sound" without actually having a DC? Adding a [hip~ 1] right before the output to get rid of the offset, I still hear some of the high-pitched sound, but not as much. I guess it's not exactly a bi-product of DC-offset?
edit: I guess I could just manually add a super-high-pitched [osc~]. Hard to get it to sound the same as the apparently non-existent high-pitch I hear at DC-offset though...
PD's scheduler, timing, control-rate, audio-rate, block-size, (sub)sample accuracy,
@EEight said:
@lacuna said:
I just see this flag on linux:
-nosleep -- spin, don't sleep (may lower latency on multi-CPUs)
Oh yes and there are startup flags for loading a different scheduler (I corrected this in my first post now)
https://puredata.info/docs/faq/commandline
-rt or -realtime -- use real-time priority
-nrt -- don't use real-time priority
-sleep -- sleep when idle, don't spin (true by default)
-nosleep -- spin, don't sleep (may lower latency on multi-CPUs)
-schedlib <file> -- plug in external scheduler
-extraflags <s> -- string argument to send schedlib
-batch -- run off-line as a batch process
-nobatch -- run interactively (true by default)
Not sure, would be interested to know too.
@EEight output of full text search of sleep with grep in pd's source folder -nri flags set:
https://pastebin.com/3mBw6Mnj
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/u_pdsend.c:86: sleep (nretry < 5 ? 1 : 5);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_stuff.h:65:extern int sys_sleepgrain;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_stuff.h:163:EXTERN void sys_microsleep(int microsec);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_stuff.h:369:EXTERN int* get_sys_sleepgrain(void);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:58:int sys_nosleep = 0; /* skip all "sleep" calls and spin instead */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:115:int* get_sys_sleepgrain() { return &sys_sleepgrain; }
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:424:"-sleepgrain <n> -- specify number of milliseconds to sleep when idle\n",
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:520:"-sleep -- sleep when idle, don't spin (true by default)\n",
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:521:"-nosleep -- spin, don't sleep (may lower latency on multi-CPUs)\n",
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:732: else if (!strcmp(*argv, "-sleepgrain"))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:737: sys_sleepgrain = 1000 * atof(argv[1]);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1242: else if (!strcmp(*argv, "-sleep"))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1244: sys_nosleep = 0;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1247: else if (!strcmp(*argv, "-nosleep"))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_main.c:1249: sys_nosleep = 1;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:202:extern int sys_nosleep;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:204:/* sleep (but cancel the sleeping if pollem is set and any file descriptors are
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:207:sleep. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:208:static int sys_domicrosleep(int microsec, int pollem)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:226: perror("microsleep select");
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:242: Sleep(microsec/1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:244: usleep(microsec);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:251: /* sleep (but if any incoming or to-gui sending to do, do that instead.)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:253:void sys_microsleep(int microsec)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:256: sys_domicrosleep(microsec, 1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_inter.c:909: int didsomething = sys_domicrosleep(0, 1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:16: correct thread synchronization (by defining THREADSIGNAL) or just sleeping
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:21: switch to usleep in s_inter.c
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:91:#include <windows.h> /* for Sleep() */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:549: sys_microsleep(sys_sleepgrain);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:550: if (!pa_stream) /* sys_microsleep() may have closed device */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:591: sys_microsleep(sys_sleepgrain);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_pa.c:592: if (!pa_stream) /* sys_microsleep() may have closed device */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_oss.c:672: sys_microsleep(2000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:105:/* if more than this sleep detected, should be more than periodsize/samplerate ??? */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:106:static double sleep_time;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:340: sleep_time = (float) alsamm_period_size/ (float) alsamm_sr;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:798: sleep(1); /* wait until the suspend flag is released */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:1336: if ((timenow = sys_getrealtime()) > (timelast + sleep_time))
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsamm.c:1342: timenow,timelast,sleep_time,(timelast + sleep_time));
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/s_audio_alsa.c:691: sys_microsleep(5000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:23:int sys_usecsincelastsleep(void);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:24:int sys_sleepgrain;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:442:will now sleep. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:454: if (sys_sleepgrain < 100)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:455: sys_sleepgrain = sys_schedadvance/4;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:456: if (sys_sleepgrain < 100)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:457: sys_sleepgrain = 100;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:458: else if (sys_sleepgrain > 5000)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:459: sys_sleepgrain = 5000;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:477: the machine sleeps. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:539: /* if even that had nothing to do, sleep. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:541: sys_microsleep(sys_sleepgrain);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:574: Sleep(1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/src/m_sched.c:576: sleep(1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptwinmm.c:67:PMEXPORT void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptwinmm.c:69: Sleep(duration);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_mach.c:128:void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_mach.c:130: usleep(duration * 1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_cf.c:137:void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptmacosx_cf.c:139: usleep(duration * 1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptlinux.c:14:of sleeping when realtime threads request a sleep of <=2ms (as a way
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptlinux.c:132:void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/ptlinux.c:134: usleep(duration * 1000);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/porttime.h:82: Pt_Sleep() pauses, allowing other threads to run.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/porttime/porttime.h:88:PMEXPORT void Pt_Sleep(int32_t duration);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/portmidi/pm_mac/pmmacosxcm.c:492: usleep((useconds_t)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portmidi/patches/mac_limit_rate_override.patch:52: usleep((useconds_t)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/win/pa_win_util.c:102:void Pa_Sleep( long msec )
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/win/pa_win_util.c:104: Sleep( msec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:108:void Pa_Sleep( long msec )
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:110:#ifdef HAVE_NANOSLEEP
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:116: nanosleep(&req, &rem);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:117: /* XXX: Try sleeping the remaining time (contained in rem) if interrupted by a signal? */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:120: { /* to usleep must be < 1000000. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:121: usleep( 999000 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:124: usleep( msec * 1000 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:599: /* Test before and after in case whatever underlying sleep call isn't interrupted by pthread_cancel */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:601: Pa_Sleep( intervalMsec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:644: PA_DEBUG(( "%s: Watchdog sleeping for %lu msecs before unthrottling\n", __FUNCTION__, th->throttledSleepTime ));
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:645: Pa_Sleep( th->throttledSleepTime );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/os/unix/pa_unix_util.c:704: Pa_Sleep( intervalMsec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:2185: unsigned long throttledSleepMsecs;
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:2565: /* time to sleep when throttling due to >100% cpu usage.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:2567: stream->throttledSleepMsecs =
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:3194: /* sleep to give other processes a go */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/wmme/pa_win_wmme.c:3195: Sleep( stream->throttledSleepMsecs );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_utilities.c:395: /* No match yet, so let's sleep and try again. */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_utilities.c:396: Pa_Sleep( 100 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.h:69:#define PA_MAC_BLIO_BUSY_WAIT_SLEEP_INTERVAL (5)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.c:454: Pa_Sleep( PA_MAC_BLIO_BUSY_WAIT_SLEEP_INTERVAL );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.c:535: Pa_Sleep( PA_MAC_BLIO_BUSY_WAIT_SLEEP_INTERVAL );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core_blocking.c:607: Pa_Sleep( msecPerBuffer );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/coreaudio/pa_mac_core.c:2722: Pa_Sleep( 100 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/asio/pa_asio.cpp:3401: Sleep(1);
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:1129: Pa_Sleep( 10 );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:2759: /* self->threading.throttledSleepTime = (unsigned long) (minFramesPerHostBuffer / sampleRate / 4 * 1000); */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:3831: Pa_Sleep( 1 ); /* avoid hot loop */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:3849: if( timeouts > 1 ) /* sometimes device times out, but normally once, so we do not sleep any time */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/hostapi/alsa/pa_linux_alsa.c:3851: Pa_Sleep( 1 ); /* avoid hot loop */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/src/common/pa_util.h:152:/* void Pa_Sleep( long msec ); must also be implemented in per-platform .c file */
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/portaudio.h:1211:/** Put the caller to sleep for at least 'msec' milliseconds. This function is
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/portaudio.h:1215: The function may sleep longer than requested so don't rely on this for accurate
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/portaudio.h:1218:void Pa_Sleep( long msec );
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/pa_win_wmme.h:64: to THREAD_PRIORITY_NORMAL and sleeps the thread if the CPU load exceeds 100%
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/portaudio/portaudio/include/pa_linux_alsa.h:91:/** Set the maximum number of times to retry opening busy device (sleeping for a
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:599:<P> In linux, a "-nosleep" flag causes Pd to poll instead of sleeping as it
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:798:<P> Fixed a thread-safety problem in sys_microsleep().
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:1224:the controlling parameter for MIDI jitter is "-sleepgrain", which specifies
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:1225:the interval of time Pd sleeps when it believes it's idle.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x5.htm:1373:<P> -sleepgrain: if you aren't using audio I/O, this can reduce time jitter in
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:488:scheduling; "-sleepgrain 1" sets the sleep grain to 1 (see under MIDI below),
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:489:and typing "-rt -sleepgrain 1" does both.
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:527:-sleepgrain <n> -- specify number of milliseconds to sleep when idle
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:573:-nosleep -- never relinquish CPU (only for multiprocessors!)
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:610:<H4> MIDI and sleepgrain</H4>
/pd-0.50-2.src.tar.gz.extracted/pd-0.50-2/doc/1.manual/x3.htm:619:<P> The "sleepgrain" controls how long (in milliseconds) Pd sleeps between
good night sweet dreams
PD's scheduler, timing, control-rate, audio-rate, block-size, (sub)sample accuracy,
Hello, 
this is going to be a long one.
After years of using PD, I am still confused about its' timing and schedueling.
I have collected many snippets from here and there about this topic,
-wich all together are really confusing to me.
*I think it is very important to understand how timing works in detail for low-level programming … *
(For example the number of heavy jittering sequencers in hard and software make me wonder what sequencers are made actually for ? lol )
This is a collection of my findings regarding this topic, a bit messy and with confused questions.
I hope we can shed some light on this.


- a)
The first time, I had issues with the PD-scheduler vs. how I thought my patch should work is described here:
https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/11615/bang-bug-when-block-1-1-1-bang-on-every-sample
The answers where:
„
[...] it's just that messages actually only process every 64 samples at the least. You can get a bang every sample with [metro 1 1 samp] but it should be noted that most pd message objects only interact with each other at 64-sample boundaries, there are some that use the elapsed logical time to get times in between though (like vsnapshot~)
also this seems like a very inefficient way to do per-sample processing..
https://github.com/sebshader/shadylib http://www.openprocessing.org/user/29118
seb-harmonik.ar posted about a year ago , last edited by seb-harmonik.ar about a year ago
• 1
whale-av
@lacuna An excellent simple explanation from @seb-harmonik.ar.
Chapter 2.5 onwards for more info....... http://puredata.info/docs/manuals/pd/x2.htm
David.
“
There is written: http://puredata.info/docs/manuals/pd/x2.htm
„2.5. scheduling
Pd uses 64-bit floating point numbers to represent time, providing sample accuracy and essentially never overflowing. Time appears to the user in milliseconds.
2.5.1. audio and messages
Audio and message processing are interleaved in Pd. Audio processing is scheduled every 64 samples at Pd's sample rate; at 44100 Hz. this gives a period of 1.45 milliseconds. You may turn DSP computation on and off by sending the "pd" object the messages "dsp 1" and "dsp 0."
In the intervals between, delays might time out or external conditions might arise (incoming MIDI, mouse clicks, or whatnot). These may cause a cascade of depth-first message passing; each such message cascade is completely run out before the next message or DSP tick is computed. Messages are never passed to objects during a DSP tick; the ticks are atomic and parameter changes sent to different objects in any given message cascade take effect simultaneously.
In the middle of a message cascade you may schedule another one at a delay of zero. This delayed cascade happens after the present cascade has finished, but at the same logical time.
2.5.2. computation load
The Pd scheduler maintains a (user-specified) lead on its computations; that is, it tries to keep ahead of real time by a small amount in order to be able to absorb unpredictable, momentary increases in computation time. This is specified using the "audiobuffer" or "frags" command line flags (see getting Pd to run ).
If Pd gets late with respect to real time, gaps (either occasional or frequent) will appear in both the input and output audio streams. On the other hand, disk strewaming objects will work correctly, so that you may use Pd as a batch program with soundfile input and/or output. The "-nogui" and "-send" startup flags are provided to aid in doing this.
Pd's "realtime" computations compete for CPU time with its own GUI, which runs as a separate process. A flow control mechanism will be provided someday to prevent this from causing trouble, but it is in any case wise to avoid having too much drawing going on while Pd is trying to make sound. If a subwindow is closed, Pd suspends sending the GUI update messages for it; but not so for miniaturized windows as of version 0.32. You should really close them when you aren't using them.
2.5.3. determinism
All message cascades that are scheduled (via "delay" and its relatives) to happen before a given audio tick will happen as scheduled regardless of whether Pd as a whole is running on time; in other words, calculation is never reordered for any real-time considerations. This is done in order to make Pd's operation deterministic.
If a message cascade is started by an external event, a time tag is given it. These time tags are guaranteed to be consistent with the times at which timeouts are scheduled and DSP ticks are computed; i.e., time never decreases. (However, either Pd or a hardware driver may lie about the physical time an input arrives; this depends on the operating system.) "Timer" objects which meaure time intervals measure them in terms of the logical time stamps of the message cascades, so that timing a "delay" object always gives exactly the theoretical value. (There is, however, a "realtime" object that measures real time, with nondeterministic results.)
If two message cascades are scheduled for the same logical time, they are carried out in the order they were scheduled.
“
[block~ smaller then 64] doesn't change the interval of message-control-domain-calculation?,
Only the size of the audio-samples calculated at once is decreased?
Is this the reason [block~] should always be … 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1, nothing inbetween, because else it would mess with the calculation every 64 samples?
How do I know which messages are handeled inbetween smaller blocksizes the 64 and which are not?
How does [vline~] execute?
Does it calculate between sample 64 and 65 a ramp of samples with a delay beforehand, calculated in samples, too - running like a "stupid array" in audio-rate?
While sample 1-64 are running, PD does audio only?
[metro 1 1 samp]
How could I have known that? The helpfile doesn't mention this. EDIT: yes, it does.
(Offtopic: actually the whole forum is full of pd-vocabular-questions)
How is this calculation being done?
But you can „use“ the metro counts every 64 samples only, don't you?
Is the timing of [metro] exact? Will the milliseconds dialed in be on point or jittering with the 64 samples interval?
Even if it is exact the upcoming calculation will happen in that 64 sample frame!?
- b )


There are [phasor~], [vphasor~] and [vphasor2~] … and [vsamphold~]
https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/10192/vphasor-and-vphasor2-subsample-accurate-phasors
“Ive been getting back into Pd lately and have been messing around with some granular stuff. A few years ago I posted a [vphasor.mmb~] abstraction that made the phase reset of [phasor~] sample-accurate using vanilla objects. Unfortunately, I'm finding that with pitch-synchronous granular synthesis, sample accuracy isn't accurate enough. There's still a little jitter that causes a little bit of noise. So I went ahead and made an external to fix this issue, and I know a lot of people have wanted this so I thought I'd share.
[vphasor~] acts just like [phasor~], except the phase resets with subsample accuracy at the moment the message is sent. I think it's about as accurate as Pd will allow, though I don't pretend to be an expert C programmer or know Pd's api that well. But it seems to be about as accurate as [vline~]. (Actually, I've found that [vline~] starts its ramp a sample early, which is some unexpected behavior.)
[…]
“
- c)



Later I discovered that PD has jittery Midi because it doesn't handle Midi at a higher priority then everything else (GUI, OSC, message-domain ect.)
EDIT:
Tryed roundtrip-midi-messages with -nogui flag:
still some jitter.
Didn't try -nosleep flag yet (see below)
- d)

So I looked into the sources of PD:
scheduler with m_mainloop()
https://github.com/pure-data/pure-data/blob/master/src/m_sched.c
And found this paper
Scheduler explained (in German):
https://iaem.at/kurse/ss19/iaa/pdscheduler.pdf/view
wich explains the interleaving of control and audio domain as in the text of @seb-harmonik.ar with some drawings
plus the distinction between the two (control vs audio / realtime vs logical time / xruns vs burst batch processing).
And the "timestamping objects" listed below.
And the mainloop:
Loop
- messages (var.duration)
- dsp (rel.const.duration)
- sleep
With
[block~ 1 1 1]
calculations in the control-domain are done between every sample? But there is still a 64 sample interval somehow?
Why is [block~ 1 1 1] more expensive? The amount of data is the same!? Is this the overhead which makes the difference? Calling up operations ect.?
Timing-relevant objects
from iemlib:
[...]
iem_blocksize~ blocksize of a window in samples
iem_samplerate~ samplerate of a window in Hertz
------------------ t3~ - time-tagged-trigger --------------------
-- inputmessages allow a sample-accurate access to signalshape --
t3_sig~ time tagged trigger sig~
t3_line~ time tagged trigger line~
--------------- t3 - time-tagged-trigger ---------------------
----------- a time-tag is prepended to each message -----------
----- so these objects allow a sample-accurate access to ------
---------- the signal-objects t3_sig~ and t3_line~ ------------
t3_bpe time tagged trigger break point envelope
t3_delay time tagged trigger delay
t3_metro time tagged trigger metronom
t3_timer time tagged trigger timer
[...]
What are different use-cases of [line~] [vline~] and [t3_line~]?
And of [phasor~] [vphasor~] and [vphasor2~]?
When should I use [block~ 1 1 1] and when shouldn't I?
[line~] starts at block boundaries defined with [block~] and ends in exact timing?
[vline~] starts the line within the block?
and [t3_line~]???? Are they some kind of interrupt? Shortcutting within sheduling???
- c) again)

https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/1114/smooth-midi-clock-jitter/2
I read this in the html help for Pd:
„
MIDI and sleepgrain
In Linux, if you ask for "pd -midioutdev 1" for instance, you get /dev/midi0 or /dev/midi00 (or even /dev/midi). "-midioutdev 45" would be /dev/midi44. In NT, device number 0 is the "MIDI mapper", which is the default MIDI device you selected from the control panel; counting from one, the device numbers are card numbers as listed by "pd -listdev."
The "sleepgrain" controls how long (in milliseconds) Pd sleeps between periods of computation. This is normally the audio buffer divided by 4, but no less than 0.1 and no more than 5. On most OSes, ingoing and outgoing MIDI is quantized to this value, so if you care about MIDI timing, reduce this to 1 or less.
„
Why is there the „sleep-time“ of PD? For energy-saving??????
This seems to slow down the whole process-chain?
Can I control this with a startup flag or from withing PD? Or only in the sources?
There is a startup-flag for loading a different scheduler, wich is not documented how to use.
- e)

[pd~] helpfile says:
ATTENTION: DSP must be running in this process for the sub-process to run. This is because its clock is slaved to audio I/O it gets from us!
Doesn't [pd~] work within a Camomile plugin!?
How are things scheduled in Camomile? How is the communication with the DAW handled?
- f)

and slightly off-topic:
There is a batch mode:
https://forum.pdpatchrepo.info/topic/11776/sigmund-fiddle-or-helmholtz-faster-than-realtime/9
EDIT:
- g)
I didn't look into it, but there is:
https://grrrr.org/research/software/
clk – Syncable clocking objects for Pure Data and Max
This library implements a number of objects for highly precise and persistently stable timing, e.g. for the control of long-lasting sound installations or other complex time-related processes.
Sorry for the mess!
Could you please help me to sort things a bit? Mabye some real-world examples would help, too.

[pix_share_read] and [pix_share_write] under windows
@whale-av, here is a log running pd with -lib Gem -verbose.
tried both 32bit and 64bit pd 0.48-1...
tried ./Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried ./Gem.dll and failed
tried ./Gem/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried ./Gem/Gem.dll and failed
tried ./Gem.pd and failed
tried ./Gem.pat and failed
tried ./Gem/Gem.pd and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem.dll and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem/Gem.dll and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem.pd and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem.pat and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/Documents/Pd/externals/Gem/Gem.pd and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem.dll and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem/Gem.dll and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem.pd and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem.pat and failed
tried C:/Users/Raphael Isdant/AppData/Roaming/Pd/Gem/Gem.pd and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem.dll and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem/Gem.dll and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem.pd and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem.pat and failed
tried C:/Program Files/Common Files/Pd/Gem/Gem.pd and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem.dll and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem/Gem.dll and succeeded
D:\\pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit\\extra\\Gem\\Gem.dll: couldn't load
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem.pd and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem.pat and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/extra/Gem/Gem.pd and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem.dll and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem/Gem.m_i386 and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem/Gem.dll and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem.pd and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem.pat and failed
tried D:/pd-0.48-1.windows.64bit/doc/5.reference/Gem/Gem.pd and failed
Gem: can't load library```PdParty, sending/recieving OSC
@toddak http://danomatika.com/code/pdparty/guide#osc-server-settings mentions setup of an osc server, but as you say there is no doc and it suggests that it only sends the phone sensor data..... but I am unsure.
It says it is inspired by TouchOSC, and the Hexler site had test patches. They used MrPeach (extended) objects though, and they will not work I think with PdParty.
It has not been updated...... https://hexler.net/docs/touchosc-getting-started-osc?android
It does mention [netsend] and [netreceive] further down, but you will have to use the vanilla methods and not the older MrPeach objects.
That can be a little more difficult.
Try this..... vanilla_bug_oscparse_solution.pd
It can cope with addresses that contain a float.
That is unlikely to be your problem though, but it will test the connection.
Chop the patch in half and test PdParty with the correct IP addresses.
David.
[small job offer] porting max external to pd
Edit 1: Took a shot porting it in this little textarea. Probably doesn't compile yet...
Edit 2: Ok, this should compile now. I haven't actually tried to instantiate it yet, though. It's possible I set it up with the wrong number of xlets.
Edit 3: Seems to instantiate ok. It appears it doesn't take signal input so the CLASS_MAINSIGNALIN macro is neccessary. Just comment that part out to make it a control signal.
Note-- in my port it's called [vb_fourses~] for the reason noted below.
I have no idea if the algorithm behaves correctly, but it does output sound.
Btw-- AFAICT you should be able to compile this external for the 64-bit version of Purr Data and it should work properly. It doesn't require a special 64-bit codepath in Pd so I commented that part out.
Btw 2-- there should probably be a "best practices" rule that states you can only name your class something that is a legal C function name. Because this class doesn't follow that practice I made a mistake in the port. Further, the user will make a mistake because I had to change the class name. If I had instead made the setup function a different name than the creator I would create an additional problem that would force users to declare the lib before using it. Bad all around, and not worth whatever benefit there is to naming a class "foo.bar" instead of "foo_bar"
/*
#include "ext.h"
#include "ext_obex.h"
#include "z_dsp.h"
#include "ext_common.h"
*/
#include "m_pd.h"
#include "math.h"
/*
a chaotic oscillator network
based on descriptions of the 'fourses system' by ciat-lonbarde
www.ciat-lonbarde.net
07.april 2013, volker b?hm
*/
#define NUMFOURSES 4
static void *myObj_class;
typedef struct {
// this is a horse... basically a ramp generator
double val;
double inc;
double dec;
double adder;
double incy, incym1; // used for smoothing
double decy, decym1; // used for smoothing
} t_horse;
typedef struct {
t_object x_obj;
double r_sr;
t_horse fourses[NUMFOURSES+2]; // four horses make a fourse...
double smoother;
t_sample x_f;
} t_myObj;
// absolute limits
static void myObj_hilim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input);
static void myObj_lolim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input);
// up and down freqs for all oscillators
static void myObj_upfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4);
static void myObj_downfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4);
static void myObj_smooth(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input);
static void myObj_info(t_myObj *x);
// DSP methods
static void myObj_dsp(t_myObj *x, t_signal **sp);
static t_int *myObj_perform(t_int *w);
//void myObj_dsp64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, short *count, double samplerate,
// long maxvectorsize, long flags);
//void myObj_perform64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, double **ins, long numins,
// double **outs, long numouts, long sampleframes, long flags, void *userparam);
//
static void *myObj_new( t_symbol *s, int argc, t_atom *argv);
//void myObj_assist(t_myObj *x, void *b, long m, long a, char *s);
void vb_fourses_tilde_setup(void) {
t_class *c;
myObj_class = class_new(gensym("vb_fourses~"), (t_newmethod)myObj_new, 0, sizeof(t_myObj),
0, A_GIMME, NULL);
c = myObj_class;
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_dsp, gensym("dsp"), A_CANT, 0);
// class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_dsp64, gensym("dsp64"), A_CANT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_smooth, gensym("smooth"), A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_hilim, gensym("hilim"), A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_lolim, gensym("lolim"), A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_upfreq, gensym("upfreq"), A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_downfreq, gensym("downfreq"), A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, A_FLOAT, 0);
class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_info, gensym("info"), 0);
//class_addmethod(c, (t_method)myObj_assist, "assist", A_CANT,0);
CLASS_MAINSIGNALIN(myObj_class, t_myObj, x_f);
// class_dspinit(c);
// class_register(CLASS_BOX, c);
post("vb_fourses~ by volker b?hm\n");
// return 0;
}
static void myObj_smooth(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input) {
// input = CLAMP(input, 0., 1.);
if (input < 0.) input = 0;
if (input > 1.) input = 1;
x->smoother = 0.01 - pow(input,0.2)*0.01;
}
static void myObj_hilim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input) {
x->fourses[0].val = input; // store global high limit in fourses[0]
}
static void myObj_lolim(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg input) {
x->fourses[5].val = input; // store global low limit in fourses[5]
}
static void myObj_upfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4) {
x->fourses[1].inc = fabs(freq1)*4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[2].inc = fabs(freq2)*4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[3].inc = fabs(freq3)*4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[4].inc = fabs(freq4)*4*x->r_sr;
}
static void myObj_downfreq(t_myObj *x, t_floatarg freq1, t_floatarg freq2, t_floatarg freq3, t_floatarg freq4) {
x->fourses[1].dec = fabs(freq1)*-4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[2].dec = fabs(freq2)*-4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[3].dec = fabs(freq3)*-4*x->r_sr;
x->fourses[4].dec = fabs(freq4)*-4*x->r_sr;
}
//#pragma mark 64bit dsp-loop ------------------
//void myObj_dsp64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, short *count, double samplerate,
// long maxvectorsize, long flags) {
// object_method(dsp64, gensym("dsp_add64"), x, myObj_perform64, 0, NULL);
//
// if(samplerate<=0) x->r_sr = 1.0/44100.0;
// else x->r_sr = 1.0/samplerate;
//
//
//}
//static void myObj_perform64(t_myObj *x, t_object *dsp64, double **ins, long numins,
// double **outs, long numouts, long sampleframes, long flags, void *userparam){
//
// t_double **output = outs;
// int vs = sampleframes;
// t_horse *fourses = x->fourses;
// double val, c, hilim, lolim;
// int i, n;
//
// if (x->x_obj.z_disabled)
// return;
//
// c = x->smoother;
// hilim = fourses[0].val;
// lolim = fourses[5].val;
//
// for(i=0; i<vs; i++)
// {
// for(n=1; n<=NUMFOURSES; n++) {
// // smoother
// fourses[n].incy = fourses[n].inc*c + fourses[n].incym1*(1-c);
// fourses[n].incym1 = fourses[n].incy;
//
// fourses[n].decy = fourses[n].dec*c + fourses[n].decym1*(1-c);
// fourses[n].decym1 = fourses[n].decy;
//
// val = fourses[n].val;
// val += fourses[n].adder;
//
// if(val <= fourses[n+1].val || val <= lolim ) {
// fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].incy;
// }
// else if( val >= fourses[n-1].val || val >= hilim ) {
// fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].decy;
// }
//
// output[n-1][i] = val;
//
// fourses[n].val = val;
// }
// }
//
// return;
//
//}
//#pragma mark 32bit dsp-loop ------------------
static void myObj_dsp(t_myObj *x, t_signal **sp)
{
dsp_add(myObj_perform, 6, x, sp[0]->s_vec, sp[1]->s_vec, sp[2]->s_vec, sp[3]->s_vec, sp[0]->s_n);
if(sp[0]->s_sr<=0)
x->r_sr = 1.0/44100.0;
else x->r_sr = 1.0/sp[0]->s_sr;
}
static t_int *myObj_perform(t_int *w)
{
t_myObj *x = (t_myObj*)(w[1]);
t_float *out1 = (float *)(w[2]);
t_float *out2 = (float *)(w[3]);
t_float *out3 = (float *)(w[4]);
t_float *out4 = (float *)(w[5]);
int vs = (int)(w[6]);
// Hm... not sure about this member. I don't think we can disable individual
// objects in Pd...
// if (x->x_obj.z_disabled)
// goto out;
t_horse *fourses = x->fourses;
double val, c, hilim, lolim;
int i, n;
c = x->smoother;
hilim = fourses[0].val;
lolim = fourses[5].val;
for(i=0; i<vs; i++)
{
for(n=1; n<=NUMFOURSES; n++) {
// smoother
fourses[n].incy = fourses[n].inc*c + fourses[n].incym1*(1-c);
fourses[n].incym1 = fourses[n].incy;
fourses[n].decy = fourses[n].dec*c + fourses[n].decym1*(1-c);
fourses[n].decym1 = fourses[n].decy;
val = fourses[n].val;
val += fourses[n].adder;
if(val <= fourses[n+1].val || val <= lolim ) {
fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].incy;
}
else if( val >= fourses[n-1].val || val >= hilim ) {
fourses[n].adder = fourses[n].decy;
}
fourses[n].val = val;
}
out1[i] = fourses[1].val;
out2[i] = fourses[2].val;
out3[i] = fourses[3].val;
out4[i] = fourses[4].val;
}
//out:
return w+7;
}
static void myObj_info(t_myObj *x) {
int i;
// only fourses 1 to 4 are used
post("----- fourses.info -------");
for(i=1; i<=NUMFOURSES; i++) {
post("fourses[%ld].val = %f", i, x->fourses[i].val);
post("fourses[%ld].inc = %f", i, x->fourses[i].inc);
post("fourses[%ld].dec = %f", i, x->fourses[i].dec);
post("fourses[%ld].adder = %f", i, x->fourses[i].adder);
}
post("------ end -------");
}
void *myObj_new(t_symbol *s, int argc, t_atom *argv)
{
t_myObj *x = (t_myObj *)pd_new(myObj_class);
// dsp_setup((t_pxobject*)x, 0);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
outlet_new((t_object *)x, &s_signal);
x->r_sr = 1.0/sys_getsr();
if(sys_getsr() <= 0)
x->r_sr = 1.0/44100.f;
int i;
for(i=1; i<=NUMFOURSES; i++) {
x->fourses[i].val = 0.;
x->fourses[i].inc = 0.01;
x->fourses[i].dec = -0.01;
x->fourses[i].adder = x->fourses[i].inc;
}
x->fourses[0].val = 1.; // dummy 'horse' only used as high limit for fourses[1]
x->fourses[5].val = -1.; // dummy 'horse' only used as low limit for fourses[4]
x->smoother = 0.01;
return x;
}
//void myObj_assist(t_myObj *x, void *b, long m, long a, char *s) {
// if (m==1) {
// switch(a) {
// case 0: sprintf (s,"message inlet"); break;
// }
// }
// else {
// switch(a) {
// case 0: sprintf (s,"(signal) signal out osc1"); break;
// case 1: sprintf(s, "(signal) signal out osc2"); break;
// case 2: sprintf(s, "(signal) signal out osc3"); break;
// case 3: sprintf(s, "(signal) signal out osc4"); break;
// }
//
// }
//}
Getting Pure data to work on Raspbian Jessie (giving pure data permission to access device?)
@pmh1d15 OSC is an IP network protocol. You will need Ethernet or Wi-Fi on the Teensy to "talk" OSC...... unless it is possible to get the Teensy to make its USB connector behave like a network port?...... maybe dangerous for future programming requirements?
At the moment it is behaving as a TTY port...... which is logical given that it is its only com port.
Either give it a network port......... https://forum.pjrc.com/threads/40238-Teensy-3-2-with-WIZ820io-and-OSC ......or convert your messages within PD from OSC to TTY data and use the USB connection.
However, looking at your OP link it seems that is exactly what is happening in "pumpsn17".
The patch [slipserial.pd] is doing the conversion to the teensy datastream.
So it is using the tty port and you should have a working system.....
Is [slipserial.pd] looking through the USB port to the pins on the Teensy...... is any voltage appearing on Teensy "S0".
More info here......
https://github.com/CNMAT/OSC
David.
mrpeach on Raspberry
Hi there,
Thanks for taking the time. I am getting a little bit frustrated here, so I guess it’s best to ask the community:
How do I get MrPeach to work on 0.47.1? I am using a Raspberry Pi 3 (running Linux version 4.9.20-v7+) and Pure Data 0.47.1.
I installed mrpeach using the “find externals” functionality. Of course I edited the path to “/home/pi/pd-externals” and created a “mrpeach” entry in the startup preferences.
Some background information: I want my Python code to “communicate” with pd but actually I do not care how they do this. OSC-Messages seem to be the easiest solution.
Well, seemed. I am a total beginner to pd
Help much appreciated 
Daniel
By the way here is the log:
tried ./osc/routeOSC.l_arm and failed
tried ./osc/routeOSC.pd_linux and failed
tried ./osc/routeOSC/routeOSC.l_arm and failed
tried ./osc/routeOSC/routeOSC.pd_linux and failed
tried ./osc/routeOSC.pd and failed
tried ./osc/routeOSC.pat and failed
tried ./osc/routeOSC/osc/routeOSC.pd and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/osc/routeOSC.l_arm and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/osc/routeOSC.pd_linux and succeeded
tried ./mrpeach.l_arm and failed
tried ./mrpeach.pd_linux and failed
tried ./mrpeach/mrpeach.l_arm and failed
tried ./mrpeach/mrpeach.pd_linux and failed
tried ./mrpeach.pd and failed
tried ./mrpeach.pat and failed
tried ./mrpeach/mrpeach.pd and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach.l_arm and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach.pd_linux and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach/mrpeach.l_arm and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach/mrpeach.pd_linux and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach.pd and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach.pat and failed
tried /home/pi/pd-externals/mrpeach/mrpeach.pd and failed
mrpeach: can't load library